- 1. 四川大學華西第二醫院藥學部(成都 610041);
- 2. 四川大學華西第二醫院循證藥學中心(成都 610041);
- 3. 國家藥品監督管理局藥物制劑體內外相關性技術研究重點實驗室(成都 610041);
- 4. 出生缺陷與相關婦兒疾病教育部重點實驗室(成都 610041);
- 5. 四川大學華西藥學院(成都 610041);
- 6. 四川大學華西臨床醫學院(成都 610041);
- 7. 四川大學華西醫院實驗醫學科(成都 610041);
- 8. 北京大學第三醫院藥劑科(北京 100191);
- 9. 四川大學華西醫院中國循證醫學中心(成都 610041);
引用本文: 刁莎, 何思頤, 劉崢, 陳哲, 程曉, 倪曉鳳, 曾力楠, 應斌武, 趙榮生, 張伶俐. 診斷試劑系統評價中性能評價指標的使用現狀與指標池構建. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2024, 24(7): 806-818. doi: 10.7507/1672-2531.202308084 復制
版權信息: ?四川大學華西醫院華西期刊社《中國循證醫學雜志》版權所有,未經授權不得轉載、改編
診斷試劑根據使用方法分為體內診斷試劑和體外診斷試劑。為規范診斷試劑注冊與備案行為,保證其安全、有效和質量可控,我國實施了分類管理。根據國家食品藥品監督管理局、國家市場監督管理總局《關于劃歸醫療器械管理的體外診斷試劑注冊事宜的通知》《醫療器械監督管理條例》《體外診斷試劑注冊與備案管理辦法》《體外診斷試劑分類規則》,體內診斷試劑按照藥品管理,體外診斷試劑按照藥品或醫療器械管理,其中用于血源篩查的體外診斷試劑、采用放射性核素標記的體外診斷試劑按照藥品管理,其余體外診斷試劑按照醫療器械分三類管理[1-4]。按照藥品管理的診斷試劑,是指對比劑、放射性診斷用藥、器官功能檢查診斷劑、診斷用生物制品,及其他利用免疫學、微生物學和分子生物學原理的診斷劑[5]。按照醫療器械管理的診斷試劑是指在疾病的預測、預防、診斷、治療監測、預后觀察和健康狀態評價的過程中,用于人體樣本體外檢測的試劑、試劑盒、校準品、質控品等,可以單獨使用,也可以與儀器、器具、設備或者系統組合使用[3]。
評價某診斷試劑,除關注方法本身的技術特性、安全性、便捷性、經濟性等諸多特征外,重點應評價該診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能,包括靈敏度、特異度等[6]。金標準是指當前公認最可靠、最有效、最佳的診斷方法,例如活檢、手術發現、病原體分離培養、長期隨訪結果等[7]。不同研究者針對同一診斷試劑的性能評價結果存在差異時,常采用系統評價對其性能進行綜合評價。然而,目前已發表的診斷試劑系統評價,無論是針對同一診斷試劑還是不同診斷試劑,對其性能評價所使用的評價指標差異較大[8-10]。本研究旨在分析診斷試劑系統評價中性能評價指標的使用現狀,并梳理、形成診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標體系清單,為相關研究提供參考。
1 資料與方法
1.1 納入與排除標準
1.1.1 研究類型
系統評價。
1.1.2 研究對象
自然人群。
1.1.3 診斷方法
待評價的不同診斷試劑。
1.1.4 結局指標
診斷性能評價指標,例如靈敏度、特異度等。
1.1.5 排除標準
① 非中、英文文獻;② 無診斷性能評價指標;③ 用診斷試劑檢測的某種血清或尿液生物學指標的性能;④ 無法獲取研究全文;⑤ 對重復發表文獻,僅提取資料最新、最全的數據。
1.2 文獻檢索策略
計算機檢索PubMed、Embase(OVID)、Cochrane Library(OVID)、CBM、VIP、WanFang Data和CNKI數據庫,搜集診斷試劑性能評價的系統評價,檢索時限為建庫至2023年4月28日。采用主題詞和關鍵詞相結合的方式,檢索字段限制為標題。英文檢索詞包括:diagnos*、screen*、systematic review;中文檢索詞包括:診斷、篩查、系統評價。以PubMed為例,其具體檢索策略見附件框1。
1.3 文獻篩選與資料提取
由2名研究者獨立篩選文獻、提取資料,如有分歧經組內討論決定。篩選文獻時首先閱讀文題和摘要,排除明顯不符合納入標準的文獻后,進一步閱讀全文,以確定最終是否納入。資料提取內容主要包括:① 納入研究的基本信息,包括研究題目、第一作者、發表時間;② 診斷試劑的特征,包括名稱、診斷用途、金標準、使用方法(體內或體外);③ 相較于金標準的性能評價指標名稱或計算方法。
1.4 文獻質量評價
由于系統評價的方法學質量評價工具AMSTAR-2僅適用于干預性研究的系統評價[11],而非診斷性研究的系統評價,且本研究僅對評價指標進行歸納、匯總,未評價納入文獻的質量。
1.5 統計分析
采用頻數(構成比)描述診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標使用現狀,采用定性合成方法,匯總診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標。
2 結果
2.1 文獻篩選流程與結果
初檢共獲得相關文獻11 701篇,其中PubMed(n=6 880)、Cochrane Library(OVID)(n=208)、Embase(OVID)(n=2 948)、CBM(n=247)、VIP(n=485)、WanFang Data(n=627)和CNKI(n=306)。參照納入與排除標準逐層篩選后,最終納入系統評價133篇[8-10,12-141]。文獻篩選流程與結果見附件圖1。
2.2 納入文獻的基本特征
納入文獻發表年份在1991―2023年之間,在中文、英文期刊發表的文獻分別為10篇、123篇,涉及的診斷試劑包括體內診斷試劑34個[例如靜脈造影劑、放射示蹤劑、結核菌素皮膚試驗(tuberculin skin test,TST)等],體外診斷試劑116個[例如幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑、陰道毛滴蟲病酶聯免疫吸附實驗(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)檢測試劑、梅毒免疫層析試紙等],見表1。
下載CSV
| 納入研究 | 診斷藥品/試劑 | 診斷用途 | 金標準 | 應用途徑 |
| Launois 2014[8] | 結直腸癌糞便潛血試驗診斷試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 體外 | |
| Maze 2019[9] | 鉤端螺旋體病全細胞側流式檢測試劑 | 鉤端螺旋體感染 | 鉤端螺旋體培養、顯微鏡凝集試驗、聚合酶聯反應(polymerase chain reaction,PCR) | 體外 |
| Hung 2023[10] | 輪狀病毒免疫層析抗原檢測試劑 | 輪狀病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Pinson 1991[12] | Technetium-99m-RBC靜脈造影劑 | 下肢深靜脈血栓 | 其他靜脈造影劑(具體不詳) | 體內 |
| Patel 2000[13] | 陰道毛滴蟲病酶聯免疫吸附實驗(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)、直接熒光抗體 (direct fluorescent antibody,DFA)檢測試劑 | 陰道毛滴蟲病 | 滴蟲培養 | 體外 |
| Cruciani 2004[14] | Parasight?-F試紙條(Becton Dickinson) | 惡性瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2004[15] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、 血清學、PCR涂片 |
體外 |
| 郭銀燕2005[16] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、快速脲酶試驗、呼氣試驗 | 體外 |
| Blacksell 2006[17] | 登革熱免疫層析法檢測試劑(Panbio Pty Ltd.) | 登革熱 | ELISA檢測試劑(Panbio Duo,Panbio IgM,MRL IgM,AFRIMS MAC)和 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2006[18] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學 | 體外 |
| 秦莉 2007[19] | 血清抗核小體抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 系統性紅斑狼瘡 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Steingart 2007[20] | 血清學抗體檢測試劑 | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2007[21] | 結核菌素皮膚試驗(tuberculin skin test,TST) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| 基于 ESAT-6 和 CFP-10 抗原的γ-干擾素釋放試驗 (interfering gamma release assay,IGRA) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| 王睿2008[22] | 血清神經元烯醇化酶酶免法(enzyme immunoassay,EIA)檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Pai 2008[23] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| 孟存仁2009[24] | Em18抗原ELISA檢測試劑 | 泡球蚴病 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| 楊渭臨2010[25] | 血清胃泌素釋放前體肽ELISA檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Branco 2010[26] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘黏性小腸梗阻 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Tucker 2010[27] | 梅毒免疫層析試紙 | 梅毒 | 血清反應素試驗、密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| 耿哲2011[28] | 血清半乳甘露聚糖ELISA檢測試劑 | 侵襲性曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Machingaidze 2011[29] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Cattamanchi 2011[30] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2011[31] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sester 2011[32] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Abba 2011[33] | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾快速檢測試劑盒 | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾 | 鏡檢、PCR | 體外 |
| Afonso 2012[34] | 急、慢性恰加斯病IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 急、慢性恰加斯病 | 多種確診方法(未具體描述) | 體外 |
| Shivkumar 2012[35] | 丙型肝炎快速和即時抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | PCR、免疫測定 | 體外 |
| Lamoth 2012[36] | β-葡聚糖抗原性測定試劑 | 侵入性霉菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chiappini 2012[37] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Fan 2012[38] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| TST | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體內 | |
| Santin 2012[39] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sinclair 2013[40] | 肺炎球菌抗原檢測試劑 | 社區獲得性肺炎 | 細菌培養、臨床癥狀、X線、痰涂片鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Sollai 2014[41] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Ruizendaal 2014[42] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Boelaert 2014[43] | 內臟利什曼疾病快速診斷試劑 | 內臟利什曼疾病 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、血清學、治療反應 | 體外 |
| Khuroo 2014[44] | 乙型肝炎表面抗原(HBsAg)快速即時診斷檢測試劑 | 乙型肝炎 | 體外 | |
| Tsapas 2014[45] | 某種膏藥 | 糖尿病神經病變 | 體外 | |
| Khuroo 2015[46] | 丙型肝炎即時診斷試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | 重組免疫母細胞試驗、HCVRNA檢測 | 體外 |
| Zhou 2015[47] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| Aggarwal 2015[48] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 胸膜結核 | 細菌培養、病理學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Campbell 2015[49] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Campbell 2015[50] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Chartrand 2015[51] | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染快速抗原檢測試劑 | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染 | 病毒培養、PCR、免疫熒光 | 體外 |
| Ferguson 2015[52] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體外 | |
| Nicholson 2015[53] | PROGENSA前列腺癌抗原3檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學、前列腺特異性抗原水平檢測、直腸指檢、磁共振成像和臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ochodo 2015[54] | 血吸蟲病循環抗原檢測試劑和尿試紙 | 血吸蟲病 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Bechet 2016[55] | 埃文斯藍色染料 | 氣管切開術患者口咽誤吸 | 視頻透視、光纖內鏡吞咽 | 體內 |
| Leeflang 2016[56] | 萊姆病ELISA血清檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Sun 2016[57] | 血小板因子4/肝素ELISA檢測試劑 | 肝素誘導的血小板較少癥 | 臨床評估、實驗室功能測定 | 體外 |
| Waddell 2016[58] | 萊姆病ELISA檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Cadieux 2016[59] | 丙型肝炎病毒感染抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎病毒感染 | RNA檢測、其他免疫檢測方法 | 體外 |
| Ceresoli 2016[60] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘連性腸梗阻 | X線 | 體內 |
| Nevis 2016[61] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 過敏性鼻炎 | 鼻激發試驗 | 體內 |
| Huo 2016[62] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-GIT) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Kahwati 2016[63] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Lu 2016[64] | TST | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-IT、T-SPOT) | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Koski 2017[65] | 流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR、病毒培養 | 體外 |
| Cuomo 2017[66] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 牛奶過敏 | 口服食物 | 體內 |
| Merckx 2017[67] | 甲型和乙型流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型和乙型流感 | PCR | 體外 |
| Wijedoru 2017[68] | 傷寒和副傷寒快速診斷試劑 | 傷寒和副傷寒 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 李文 2018[69] | 葉酸受體介導的宮頸特殊染色劑 | 宮頸癌篩查 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Ning 2018[70] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染ELISA快速檢測試劑盒 | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Orme 2018[71] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染熒光酶免疫分析試 劑盒 |
結締組織病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Faust 2018[72] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、GFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Greenaway 2018[73] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-2G、QFT-3G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Pin Vieito 2018[74] | 結直腸癌糞便免疫化學定量檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| Wen 2018[75] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 抗酸染色、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Willemse 2018[76] | TST、抗酸染色試劑 | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體外 | |
| Yerlikaya 2018[77] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Treglia 2019[78] | PET/CT示蹤劑,包括:氟-18氟脫氧葡萄糖[(18)F-FDG]、碳-11甲硫氨酸[(11)c-甲硫氨酸]、氟-18氟乙基酪氨酸[(18)F-FET]、氟-18二羥基苯丙氨酸[(18)F-FDOPA]、氟-18氟胸腺嘧啶[(18)F-FLT]和碳-11膽堿[(11)c-膽堿] | 腦腫瘤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Zanetti 2019[79] | 抗利什曼病抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 皮膚利什曼病 | Montenegro皮膚試驗、鏡檢、培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 高波 2019[80] | 示蹤劑(99mTc-亞錫植酸鈉和美蘭) | 乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢示蹤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2019[81] | 糞便隱血檢測試劑 | 胃腸道疾病(腹痛、腹瀉、便秘和缺鐵性貧血等) | 內窺鏡、結腸鏡、糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Stonestreet 2019[82] | 糞便免疫化學血紅蛋白檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| V?rhendi 2020[83] | 幽門螺桿菌診斷試劑,包括快速尿素酶試驗、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學、糞便抗原試驗 | 消化性潰瘍出血 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Jullien 2020[84] | 鼠疫快速檢測試劑 | 鼠疫 | 細菌培養、PCR、配對血清學 | 體外 |
| Volpe Chaves 2020[85] | 曲霉特異性IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 慢性肺曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Khandker 2021[86] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Kim 2021[87] | 甲苯胺藍 | 口腔癌及癌前病變 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2021[88] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lee 2021[89] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2021[90] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Zefenkey 2021[91] | 碳青霉烯酶快速檢測試劑 | 產碳青霉烯酶腸桿菌感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yang 2021[92] | 全氟丁烷超聲造影劑 | 肝細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Yoon 2021[93] | 諾如病毒免疫層析檢測試劑 | 諾如病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Alabousi 2021[94] | 腸內造影劑 | 成人穿透性外傷腹部骨盆CT | 手術、臨床或影像學隨訪 | 體內 |
| Albaharna 2021[95] | 局部鼻內熒光素 | 診斷和定位鼻腦脊液泄漏 | 實驗室檢查、放射學檢查 | 體內 |
| Alberts 2021[96] | 放射示蹤劑 | 復發性前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Angel-Müller 2021[97] | 梅毒即時檢測試劑 | 梅毒 | 密螺旋體和非密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2021[98] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Okpua 2021[99] | 前列腺特異性抗原檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Lima 2021[100] | 自體熒光劑 | 口腔鱗狀細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Oh 2021[101] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2021[102] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[103] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[104] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Fairley 2021[105] | 類鼻疽病ELISA檢測試劑 | 類鼻疽病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| 程曉2022[106] | 重組結核桿菌融合蛋白(EC) | 結核分枝桿菌感染和結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Arshadi 2022[107] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Labiste 2022[108] | 含釓造影劑 | 闌尾骨骼骨髓炎 | 臨床特征、手術、組織學、病理學 | 體內 |
| Zhang 2022[109] | T-SPOT.TB | 結核性胸膜炎 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2022[110] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、細胞培養 | 體外 |
| Candia-Puma 2022[111] | 恰加斯病ELISA檢測試劑 | 恰加斯病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2022[112] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Duncan 2022[113] | SARS-CoV-2核酸擴增檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、逆轉錄酶環介導的等溫擴增、轉錄介導擴增 | 體外 |
| Falconer 2022[114] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Frempong 2022[115] | 傷寒快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 傷寒 | 血液培養 | 體外 |
| Fujita-Rohwerder 2022[116] | SARS-CoV-2快速即時抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、臨床癥狀、臨床隨訪 | 體外 |
| Gentilotti 2022[117] | 急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染即時檢測 試劑 |
急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Muzembo 2022[118] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Pandey 2022[119] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Petnak 2022[120] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 涂片陰性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Ren 2022[121] | IGRA | 骨關節結核 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Romero 2022[122] | 麻風病即時診斷檢測試劑 | 麻風病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Seid 2022[123] | 脂阿拉伯甘露聚糖(LAM)抗原檢測試劑 | 結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Shi 2022[124] | TBAg刺激的IFN-γ(IGRA)和未刺激的IFN-γ檢測 | 結核性腦膜炎 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Shim 2022[125] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷檢測 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2022[126] | SARS-CoV-2感染快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Jullien 2022[127] | Luminex NxTAG RPP?(多重呼吸道病原體檢測試劑) | 呼吸道合胞病毒或甲/乙流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Khalid 2022[128] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lippi 2022[129] | DiaSorin聯合SARS-CoV-2抗原免疫測定 試劑 |
SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2022[130] | 放射性示蹤劑 | 前列腺癌生化復發 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Mahon 2022[131] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Teeuw 2022[132] | 尿試紙 | 子癇前期蛋白尿 | PCR、24小時尿液采集中蛋白質含量≥ 300 mg |
體外 |
| Wen 2022[133] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核性腦膜炎 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Xie 2022[134] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yimam 2022[135] | 瘧疾新型超敏快速診斷檢測試劑、常規快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| 鄒小青2023[136] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB | 活動性結核病 | 病原學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ortiz-Brizuela 2023[137] | IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-Plus CLIA、QIAreach 、Wantai TB-IGRA、Standard E TB-Feron、T-SPOT.TB/T-Cell Select) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Karlafti 2023[138] | SARS-CoV-2鼻腔快速抗原自檢試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dagens 2023[139] | 埃博拉病毒快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | 埃博拉病毒 | PCR | 體外 |
| Zhang 2023[140] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Zangiabadian 2023[141] | 艱難梭菌快速診斷檢測試劑 | 艱難梭菌感染 | 產毒培養 | 體外 |
2.3 評價指標體系的使用現狀與構建
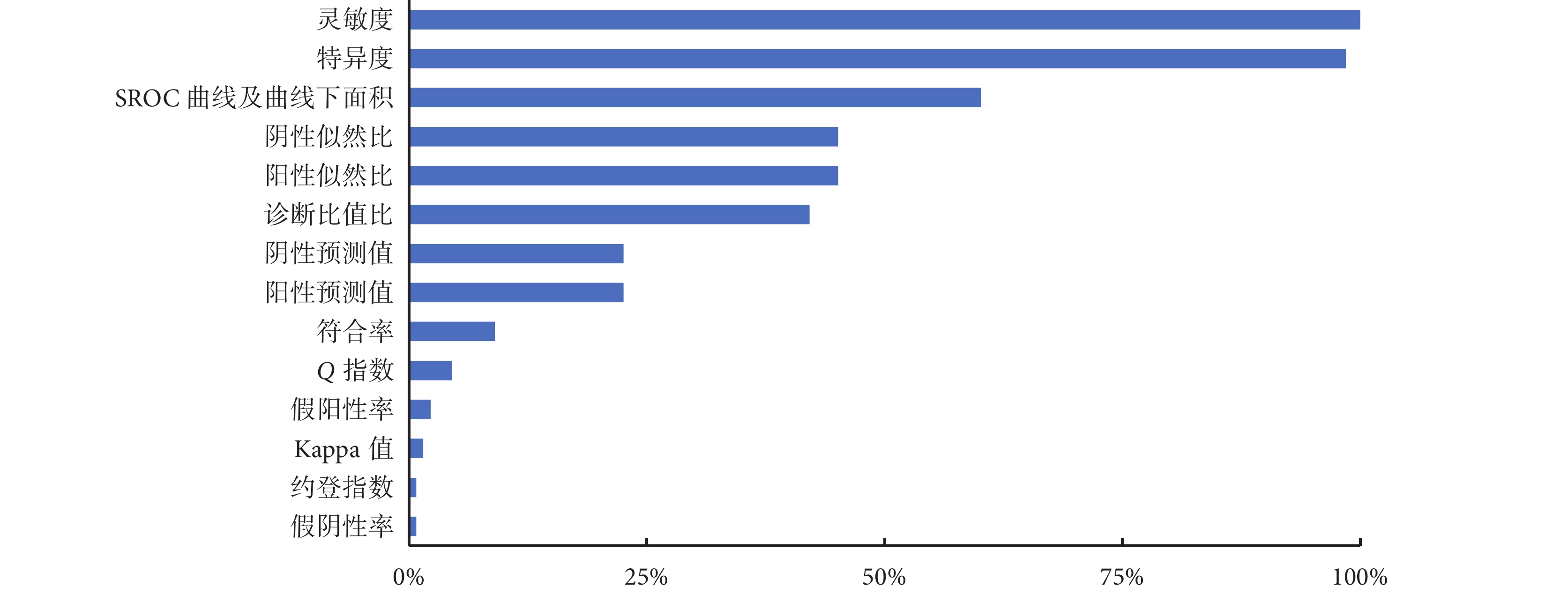
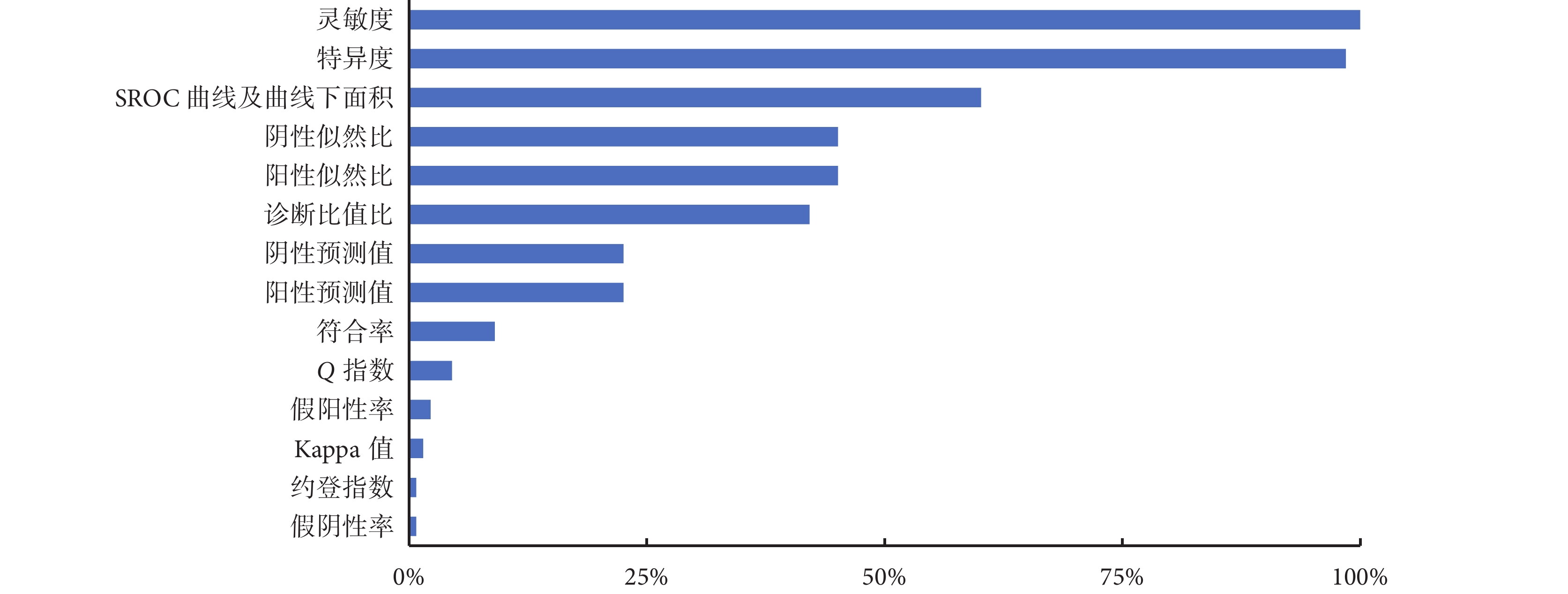
納入文獻在評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能時,使用頻率超過50%的評價指標為靈敏度(133/133,100.0%)、特異度(131/133,98.5%)和SROC曲線下面積(area under curve,AUC)(80/133,60.2%),使用頻率不足5%的評價指標為Q指數(6/133,4.5%)、假陽性率(3/133,2.3%)、Kappa值(2/133,1.5%)、假陰性率(1/133,0.8%)和約登指數(1/133,0.8%),見圖1。
基于本研究結果,開展診斷試劑系統評價時,可通過繪制四格表,提取各原始研究中該診斷試劑相較于金標準的真陽性、假陰性、真陰性和假陽性人數,從真實性、預測性兩個維度評價性能,可使用的評價指標共14個,見表2、表3。
下載CSV
| 診斷試劑 | 金標準 | 合計 | |
| 患者 | 非患者 | ||
| 陽性 | a(真陽性) | b(假陽性) | a+b |
| 陰性 | c(假陰性) | d(真陰性) | c+d |
| 合計 | a+c | b+d | a+b+c+d |
下載CSV
| 評價維度與指標 | 指標含義 | 計算公式 |
| 真實性:診斷結果與金標準相符合的程度 | ||
| 靈敏度(真陽性率或敏感度)(sensitivity,Sen) | 診斷試劑將患者正確判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現患者的能力 | a/(a+c) |
| 假陰性率(漏診率)(false negative rate,FNR) | 診斷試劑將患者錯誤判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑漏診患者的能力 | c/(a+c) |
| 特異度(真陰性率)(specificity,Spe) | 診斷試劑將非患者正確判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現非患者的能力 | d/(b+d) |
| 假陽性率(誤診率)(false positive rate,FPR) | 診斷試劑將非患者錯誤判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑誤診患者的能力 | b/(b+d) |
| 符合率(一致率或準確率)(accuracy,Ac) | 診斷試劑正確判斷患者、非患者的人數占總人數的比例,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的能力 | (a+d)/(a+b+c+d) |
| 約登指數(正確指數)(Youden's index) | 靈敏度與特異度之和減1,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的總能力 | 靈敏度+特異度?1 |
| 陽性似然比(positive likelihood ratio,+LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陽性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | 靈敏度/(1?特異度) |
| 陰性似然比(negative likelihood ratio,?LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陰性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | (1?靈敏度)/特異度 |
| 診斷比值比(diagnostic odds ratio,DOR) | 患者中診斷試劑判斷為陽性的比值與非患者中試劑判斷為陽性的比值之比,是融合靈敏度、特異度、陽性似然比和陰性似然比的綜合指標 | (a×d)/(b×c) |
| Kappa值 | 診斷試劑與金標準結果的一致性 | 無 |
| 綜合受試者工作特征曲線(symmetric receiver operator characteristic curve,SROC)及曲線下面積(the area under the curve,AUC) | 以靈敏度為y軸,1-特異度為x軸匯成的曲線,綜合評價診斷試劑的準確性 | 無 |
| Q指數 | SROC曲線與直線(靈敏度=特異度)相交處的靈敏度 | 無 |
| 預測性:應用診斷結果估計患者患病或不患病的可能性 | ||
| 陽性預測值(positive predictive value,PPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陽性的人數中患者的比例 | a/(a+b) |
| 陰性預測值(negative predictive value,NPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陰性的人數中非患者的比例 | d/(c+d) |
3 討論
診斷試劑是輔助臨床診療的重要手段,因為在臨床診療過程中,由于許多疾病的標準診斷方法復雜、可能給患者造成創傷、需要復雜的實驗室設備等,醫務人員在臨床診斷疾病時可能不采用金標準,而用診斷試劑替代。診斷試劑是否能準確判斷患者或非患者,將對后續的臨床診療方案產生重要影響,因此,除關注診斷試劑的技術特性、安全性和經濟性等特征外,必須將其與金標準進行比較,以評價診斷性能。
研究者可通過開展病例-對照研究、隊列研究,評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能,使所有研究對象同步、獨立、盲法進行診斷試劑和金標準的檢測[142]。然而,由于研究對象特征、樣本量等因素的影響,針對同一研究問題,不同研究者得出的結論可能存在差異,此時可利用系統評價得出綜合結論。根據證據金字塔可類推[7],診斷試劑系統評價的證據等級高于單個研究,因此,診斷試劑系統評價使用的評價指標是否全面,將直接影響對診斷試劑性能的綜合判斷。
基于本研究結果,已發表的診斷試劑系統評價使用的評價指標以靈敏度、特異度和AUC為主。靈敏度又稱真陽性率,是指實際患病且診斷試劑判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現患者的能力,該取值越大越好[6];與之對應的評價指標則是特異度,是指實際未患病且診斷試劑判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現非患者的能力,該取值越大越好[6]。診斷試劑系統評價中的SROC曲線是性能的總體表現,是對同一檢測指標的多個不同試驗進行Meta分析、根據效應量權重獲得的曲線,AUC是SROC曲線下面積,與靈敏度、特異度有關,該取值越大越好[142]。上述3個指標側重評價診斷試劑判斷結果與金標準的符合程度,但僅使用上述指標,不能全面評價診斷試劑性能。例如評價診斷試劑判斷結果與金標準的一致性,需使用Kappa值;評價診斷試劑的預測價值,需使用陽性預測值和陰性預測值。英國國家健康與臨床卓越研究所[143]、伊朗馬什哈德大學核醫學研究中心[144]分別于2011年、2016年發布指導診斷試驗系統評價的實踐指南,提及的評價指標除靈敏度、特異度和AUC外,還包括似然比、預測值和診斷比值比,上述指標均包含在表3指標體系清單中。
然而,已發表的診斷試劑系統評價使用較少的評價指標,如:Q指數、假陽性率、假陰性率、約登指數和Kappa值,在全面評價診斷試劑性能時仍具有一定作用。Q指數是SROC曲線與直線(靈敏度=特異度)相交處的靈敏度,該取值越大越好;假陽性率和假陰性率可分別用于衡量診斷試劑的誤診和漏診能力,該取值越小越好;約登指數是診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的總能力,取值范圍為0~1,常用于不同診斷試劑間的比較,該取值越大越好;Kappa值反映診斷試劑與金標準結果的一致性,取值范圍為0~1,≥0.75表示一致性較高。
本研究的局限:① 檢索字段僅限制在標題,可能遺漏部分文獻;② 限于語言限制,僅納入中、英文文獻;③ 部分文獻因無法獲得全文,暫未納入。
綜上所述,系統評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能時,僅使用單一指標不能全面反映診斷性能,應在數據可及的情況下,從真實性、預測性兩個維度開展評價,各維度選擇評價內容不同的指標,呈互補關系的指標選則其一即可,例如真實性維度有評價指標12個,但由于靈敏度與假陰性率互補,即靈敏度=1?假陰性率,從中選擇1個指標即可。后續仍需基于專家共識形成診斷試劑性能評價的技術指南,以規范診斷試劑性能評價指標報告模式。
診斷試劑根據使用方法分為體內診斷試劑和體外診斷試劑。為規范診斷試劑注冊與備案行為,保證其安全、有效和質量可控,我國實施了分類管理。根據國家食品藥品監督管理局、國家市場監督管理總局《關于劃歸醫療器械管理的體外診斷試劑注冊事宜的通知》《醫療器械監督管理條例》《體外診斷試劑注冊與備案管理辦法》《體外診斷試劑分類規則》,體內診斷試劑按照藥品管理,體外診斷試劑按照藥品或醫療器械管理,其中用于血源篩查的體外診斷試劑、采用放射性核素標記的體外診斷試劑按照藥品管理,其余體外診斷試劑按照醫療器械分三類管理[1-4]。按照藥品管理的診斷試劑,是指對比劑、放射性診斷用藥、器官功能檢查診斷劑、診斷用生物制品,及其他利用免疫學、微生物學和分子生物學原理的診斷劑[5]。按照醫療器械管理的診斷試劑是指在疾病的預測、預防、診斷、治療監測、預后觀察和健康狀態評價的過程中,用于人體樣本體外檢測的試劑、試劑盒、校準品、質控品等,可以單獨使用,也可以與儀器、器具、設備或者系統組合使用[3]。
評價某診斷試劑,除關注方法本身的技術特性、安全性、便捷性、經濟性等諸多特征外,重點應評價該診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能,包括靈敏度、特異度等[6]。金標準是指當前公認最可靠、最有效、最佳的診斷方法,例如活檢、手術發現、病原體分離培養、長期隨訪結果等[7]。不同研究者針對同一診斷試劑的性能評價結果存在差異時,常采用系統評價對其性能進行綜合評價。然而,目前已發表的診斷試劑系統評價,無論是針對同一診斷試劑還是不同診斷試劑,對其性能評價所使用的評價指標差異較大[8-10]。本研究旨在分析診斷試劑系統評價中性能評價指標的使用現狀,并梳理、形成診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標體系清單,為相關研究提供參考。
1 資料與方法
1.1 納入與排除標準
1.1.1 研究類型
系統評價。
1.1.2 研究對象
自然人群。
1.1.3 診斷方法
待評價的不同診斷試劑。
1.1.4 結局指標
診斷性能評價指標,例如靈敏度、特異度等。
1.1.5 排除標準
① 非中、英文文獻;② 無診斷性能評價指標;③ 用診斷試劑檢測的某種血清或尿液生物學指標的性能;④ 無法獲取研究全文;⑤ 對重復發表文獻,僅提取資料最新、最全的數據。
1.2 文獻檢索策略
計算機檢索PubMed、Embase(OVID)、Cochrane Library(OVID)、CBM、VIP、WanFang Data和CNKI數據庫,搜集診斷試劑性能評價的系統評價,檢索時限為建庫至2023年4月28日。采用主題詞和關鍵詞相結合的方式,檢索字段限制為標題。英文檢索詞包括:diagnos*、screen*、systematic review;中文檢索詞包括:診斷、篩查、系統評價。以PubMed為例,其具體檢索策略見附件框1。
1.3 文獻篩選與資料提取
由2名研究者獨立篩選文獻、提取資料,如有分歧經組內討論決定。篩選文獻時首先閱讀文題和摘要,排除明顯不符合納入標準的文獻后,進一步閱讀全文,以確定最終是否納入。資料提取內容主要包括:① 納入研究的基本信息,包括研究題目、第一作者、發表時間;② 診斷試劑的特征,包括名稱、診斷用途、金標準、使用方法(體內或體外);③ 相較于金標準的性能評價指標名稱或計算方法。
1.4 文獻質量評價
由于系統評價的方法學質量評價工具AMSTAR-2僅適用于干預性研究的系統評價[11],而非診斷性研究的系統評價,且本研究僅對評價指標進行歸納、匯總,未評價納入文獻的質量。
1.5 統計分析
采用頻數(構成比)描述診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標使用現狀,采用定性合成方法,匯總診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標。
2 結果
2.1 文獻篩選流程與結果
初檢共獲得相關文獻11 701篇,其中PubMed(n=6 880)、Cochrane Library(OVID)(n=208)、Embase(OVID)(n=2 948)、CBM(n=247)、VIP(n=485)、WanFang Data(n=627)和CNKI(n=306)。參照納入與排除標準逐層篩選后,最終納入系統評價133篇[8-10,12-141]。文獻篩選流程與結果見附件圖1。
2.2 納入文獻的基本特征
納入文獻發表年份在1991―2023年之間,在中文、英文期刊發表的文獻分別為10篇、123篇,涉及的診斷試劑包括體內診斷試劑34個[例如靜脈造影劑、放射示蹤劑、結核菌素皮膚試驗(tuberculin skin test,TST)等],體外診斷試劑116個[例如幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑、陰道毛滴蟲病酶聯免疫吸附實驗(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)檢測試劑、梅毒免疫層析試紙等],見表1。
下載CSV
| 納入研究 | 診斷藥品/試劑 | 診斷用途 | 金標準 | 應用途徑 |
| Launois 2014[8] | 結直腸癌糞便潛血試驗診斷試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 體外 | |
| Maze 2019[9] | 鉤端螺旋體病全細胞側流式檢測試劑 | 鉤端螺旋體感染 | 鉤端螺旋體培養、顯微鏡凝集試驗、聚合酶聯反應(polymerase chain reaction,PCR) | 體外 |
| Hung 2023[10] | 輪狀病毒免疫層析抗原檢測試劑 | 輪狀病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Pinson 1991[12] | Technetium-99m-RBC靜脈造影劑 | 下肢深靜脈血栓 | 其他靜脈造影劑(具體不詳) | 體內 |
| Patel 2000[13] | 陰道毛滴蟲病酶聯免疫吸附實驗(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)、直接熒光抗體 (direct fluorescent antibody,DFA)檢測試劑 | 陰道毛滴蟲病 | 滴蟲培養 | 體外 |
| Cruciani 2004[14] | Parasight?-F試紙條(Becton Dickinson) | 惡性瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2004[15] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、 血清學、PCR涂片 |
體外 |
| 郭銀燕2005[16] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、快速脲酶試驗、呼氣試驗 | 體外 |
| Blacksell 2006[17] | 登革熱免疫層析法檢測試劑(Panbio Pty Ltd.) | 登革熱 | ELISA檢測試劑(Panbio Duo,Panbio IgM,MRL IgM,AFRIMS MAC)和 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2006[18] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學 | 體外 |
| 秦莉 2007[19] | 血清抗核小體抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 系統性紅斑狼瘡 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Steingart 2007[20] | 血清學抗體檢測試劑 | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2007[21] | 結核菌素皮膚試驗(tuberculin skin test,TST) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| 基于 ESAT-6 和 CFP-10 抗原的γ-干擾素釋放試驗 (interfering gamma release assay,IGRA) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| 王睿2008[22] | 血清神經元烯醇化酶酶免法(enzyme immunoassay,EIA)檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Pai 2008[23] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| 孟存仁2009[24] | Em18抗原ELISA檢測試劑 | 泡球蚴病 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| 楊渭臨2010[25] | 血清胃泌素釋放前體肽ELISA檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Branco 2010[26] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘黏性小腸梗阻 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Tucker 2010[27] | 梅毒免疫層析試紙 | 梅毒 | 血清反應素試驗、密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| 耿哲2011[28] | 血清半乳甘露聚糖ELISA檢測試劑 | 侵襲性曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Machingaidze 2011[29] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Cattamanchi 2011[30] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2011[31] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sester 2011[32] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Abba 2011[33] | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾快速檢測試劑盒 | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾 | 鏡檢、PCR | 體外 |
| Afonso 2012[34] | 急、慢性恰加斯病IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 急、慢性恰加斯病 | 多種確診方法(未具體描述) | 體外 |
| Shivkumar 2012[35] | 丙型肝炎快速和即時抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | PCR、免疫測定 | 體外 |
| Lamoth 2012[36] | β-葡聚糖抗原性測定試劑 | 侵入性霉菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chiappini 2012[37] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Fan 2012[38] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| TST | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體內 | |
| Santin 2012[39] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sinclair 2013[40] | 肺炎球菌抗原檢測試劑 | 社區獲得性肺炎 | 細菌培養、臨床癥狀、X線、痰涂片鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Sollai 2014[41] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Ruizendaal 2014[42] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Boelaert 2014[43] | 內臟利什曼疾病快速診斷試劑 | 內臟利什曼疾病 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、血清學、治療反應 | 體外 |
| Khuroo 2014[44] | 乙型肝炎表面抗原(HBsAg)快速即時診斷檢測試劑 | 乙型肝炎 | 體外 | |
| Tsapas 2014[45] | 某種膏藥 | 糖尿病神經病變 | 體外 | |
| Khuroo 2015[46] | 丙型肝炎即時診斷試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | 重組免疫母細胞試驗、HCVRNA檢測 | 體外 |
| Zhou 2015[47] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| Aggarwal 2015[48] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 胸膜結核 | 細菌培養、病理學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Campbell 2015[49] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Campbell 2015[50] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Chartrand 2015[51] | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染快速抗原檢測試劑 | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染 | 病毒培養、PCR、免疫熒光 | 體外 |
| Ferguson 2015[52] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體外 | |
| Nicholson 2015[53] | PROGENSA前列腺癌抗原3檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學、前列腺特異性抗原水平檢測、直腸指檢、磁共振成像和臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ochodo 2015[54] | 血吸蟲病循環抗原檢測試劑和尿試紙 | 血吸蟲病 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Bechet 2016[55] | 埃文斯藍色染料 | 氣管切開術患者口咽誤吸 | 視頻透視、光纖內鏡吞咽 | 體內 |
| Leeflang 2016[56] | 萊姆病ELISA血清檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Sun 2016[57] | 血小板因子4/肝素ELISA檢測試劑 | 肝素誘導的血小板較少癥 | 臨床評估、實驗室功能測定 | 體外 |
| Waddell 2016[58] | 萊姆病ELISA檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Cadieux 2016[59] | 丙型肝炎病毒感染抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎病毒感染 | RNA檢測、其他免疫檢測方法 | 體外 |
| Ceresoli 2016[60] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘連性腸梗阻 | X線 | 體內 |
| Nevis 2016[61] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 過敏性鼻炎 | 鼻激發試驗 | 體內 |
| Huo 2016[62] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-GIT) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Kahwati 2016[63] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Lu 2016[64] | TST | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-IT、T-SPOT) | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Koski 2017[65] | 流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR、病毒培養 | 體外 |
| Cuomo 2017[66] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 牛奶過敏 | 口服食物 | 體內 |
| Merckx 2017[67] | 甲型和乙型流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型和乙型流感 | PCR | 體外 |
| Wijedoru 2017[68] | 傷寒和副傷寒快速診斷試劑 | 傷寒和副傷寒 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 李文 2018[69] | 葉酸受體介導的宮頸特殊染色劑 | 宮頸癌篩查 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Ning 2018[70] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染ELISA快速檢測試劑盒 | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Orme 2018[71] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染熒光酶免疫分析試 劑盒 |
結締組織病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Faust 2018[72] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、GFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Greenaway 2018[73] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-2G、QFT-3G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Pin Vieito 2018[74] | 結直腸癌糞便免疫化學定量檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| Wen 2018[75] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 抗酸染色、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Willemse 2018[76] | TST、抗酸染色試劑 | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體外 | |
| Yerlikaya 2018[77] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Treglia 2019[78] | PET/CT示蹤劑,包括:氟-18氟脫氧葡萄糖[(18)F-FDG]、碳-11甲硫氨酸[(11)c-甲硫氨酸]、氟-18氟乙基酪氨酸[(18)F-FET]、氟-18二羥基苯丙氨酸[(18)F-FDOPA]、氟-18氟胸腺嘧啶[(18)F-FLT]和碳-11膽堿[(11)c-膽堿] | 腦腫瘤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Zanetti 2019[79] | 抗利什曼病抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 皮膚利什曼病 | Montenegro皮膚試驗、鏡檢、培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 高波 2019[80] | 示蹤劑(99mTc-亞錫植酸鈉和美蘭) | 乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢示蹤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2019[81] | 糞便隱血檢測試劑 | 胃腸道疾病(腹痛、腹瀉、便秘和缺鐵性貧血等) | 內窺鏡、結腸鏡、糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Stonestreet 2019[82] | 糞便免疫化學血紅蛋白檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| V?rhendi 2020[83] | 幽門螺桿菌診斷試劑,包括快速尿素酶試驗、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學、糞便抗原試驗 | 消化性潰瘍出血 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Jullien 2020[84] | 鼠疫快速檢測試劑 | 鼠疫 | 細菌培養、PCR、配對血清學 | 體外 |
| Volpe Chaves 2020[85] | 曲霉特異性IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 慢性肺曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Khandker 2021[86] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Kim 2021[87] | 甲苯胺藍 | 口腔癌及癌前病變 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2021[88] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lee 2021[89] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2021[90] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Zefenkey 2021[91] | 碳青霉烯酶快速檢測試劑 | 產碳青霉烯酶腸桿菌感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yang 2021[92] | 全氟丁烷超聲造影劑 | 肝細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Yoon 2021[93] | 諾如病毒免疫層析檢測試劑 | 諾如病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Alabousi 2021[94] | 腸內造影劑 | 成人穿透性外傷腹部骨盆CT | 手術、臨床或影像學隨訪 | 體內 |
| Albaharna 2021[95] | 局部鼻內熒光素 | 診斷和定位鼻腦脊液泄漏 | 實驗室檢查、放射學檢查 | 體內 |
| Alberts 2021[96] | 放射示蹤劑 | 復發性前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Angel-Müller 2021[97] | 梅毒即時檢測試劑 | 梅毒 | 密螺旋體和非密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2021[98] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Okpua 2021[99] | 前列腺特異性抗原檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Lima 2021[100] | 自體熒光劑 | 口腔鱗狀細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Oh 2021[101] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2021[102] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[103] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[104] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Fairley 2021[105] | 類鼻疽病ELISA檢測試劑 | 類鼻疽病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| 程曉2022[106] | 重組結核桿菌融合蛋白(EC) | 結核分枝桿菌感染和結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Arshadi 2022[107] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Labiste 2022[108] | 含釓造影劑 | 闌尾骨骼骨髓炎 | 臨床特征、手術、組織學、病理學 | 體內 |
| Zhang 2022[109] | T-SPOT.TB | 結核性胸膜炎 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2022[110] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、細胞培養 | 體外 |
| Candia-Puma 2022[111] | 恰加斯病ELISA檢測試劑 | 恰加斯病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2022[112] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Duncan 2022[113] | SARS-CoV-2核酸擴增檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、逆轉錄酶環介導的等溫擴增、轉錄介導擴增 | 體外 |
| Falconer 2022[114] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Frempong 2022[115] | 傷寒快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 傷寒 | 血液培養 | 體外 |
| Fujita-Rohwerder 2022[116] | SARS-CoV-2快速即時抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、臨床癥狀、臨床隨訪 | 體外 |
| Gentilotti 2022[117] | 急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染即時檢測 試劑 |
急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Muzembo 2022[118] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Pandey 2022[119] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Petnak 2022[120] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 涂片陰性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Ren 2022[121] | IGRA | 骨關節結核 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Romero 2022[122] | 麻風病即時診斷檢測試劑 | 麻風病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Seid 2022[123] | 脂阿拉伯甘露聚糖(LAM)抗原檢測試劑 | 結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Shi 2022[124] | TBAg刺激的IFN-γ(IGRA)和未刺激的IFN-γ檢測 | 結核性腦膜炎 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Shim 2022[125] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷檢測 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2022[126] | SARS-CoV-2感染快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Jullien 2022[127] | Luminex NxTAG RPP?(多重呼吸道病原體檢測試劑) | 呼吸道合胞病毒或甲/乙流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Khalid 2022[128] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lippi 2022[129] | DiaSorin聯合SARS-CoV-2抗原免疫測定 試劑 |
SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2022[130] | 放射性示蹤劑 | 前列腺癌生化復發 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Mahon 2022[131] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Teeuw 2022[132] | 尿試紙 | 子癇前期蛋白尿 | PCR、24小時尿液采集中蛋白質含量≥ 300 mg |
體外 |
| Wen 2022[133] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核性腦膜炎 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Xie 2022[134] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yimam 2022[135] | 瘧疾新型超敏快速診斷檢測試劑、常規快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| 鄒小青2023[136] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB | 活動性結核病 | 病原學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ortiz-Brizuela 2023[137] | IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-Plus CLIA、QIAreach 、Wantai TB-IGRA、Standard E TB-Feron、T-SPOT.TB/T-Cell Select) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Karlafti 2023[138] | SARS-CoV-2鼻腔快速抗原自檢試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dagens 2023[139] | 埃博拉病毒快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | 埃博拉病毒 | PCR | 體外 |
| Zhang 2023[140] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Zangiabadian 2023[141] | 艱難梭菌快速診斷檢測試劑 | 艱難梭菌感染 | 產毒培養 | 體外 |
2.3 評價指標體系的使用現狀與構建
納入文獻在評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能時,使用頻率超過50%的評價指標為靈敏度(133/133,100.0%)、特異度(131/133,98.5%)和SROC曲線下面積(area under curve,AUC)(80/133,60.2%),使用頻率不足5%的評價指標為Q指數(6/133,4.5%)、假陽性率(3/133,2.3%)、Kappa值(2/133,1.5%)、假陰性率(1/133,0.8%)和約登指數(1/133,0.8%),見圖1。
基于本研究結果,開展診斷試劑系統評價時,可通過繪制四格表,提取各原始研究中該診斷試劑相較于金標準的真陽性、假陰性、真陰性和假陽性人數,從真實性、預測性兩個維度評價性能,可使用的評價指標共14個,見表2、表3。
下載CSV
| 診斷試劑 | 金標準 | 合計 | |
| 患者 | 非患者 | ||
| 陽性 | a(真陽性) | b(假陽性) | a+b |
| 陰性 | c(假陰性) | d(真陰性) | c+d |
| 合計 | a+c | b+d | a+b+c+d |
下載CSV
| 評價維度與指標 | 指標含義 | 計算公式 |
| 真實性:診斷結果與金標準相符合的程度 | ||
| 靈敏度(真陽性率或敏感度)(sensitivity,Sen) | 診斷試劑將患者正確判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現患者的能力 | a/(a+c) |
| 假陰性率(漏診率)(false negative rate,FNR) | 診斷試劑將患者錯誤判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑漏診患者的能力 | c/(a+c) |
| 特異度(真陰性率)(specificity,Spe) | 診斷試劑將非患者正確判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現非患者的能力 | d/(b+d) |
| 假陽性率(誤診率)(false positive rate,FPR) | 診斷試劑將非患者錯誤判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑誤診患者的能力 | b/(b+d) |
| 符合率(一致率或準確率)(accuracy,Ac) | 診斷試劑正確判斷患者、非患者的人數占總人數的比例,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的能力 | (a+d)/(a+b+c+d) |
| 約登指數(正確指數)(Youden's index) | 靈敏度與特異度之和減1,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的總能力 | 靈敏度+特異度?1 |
| 陽性似然比(positive likelihood ratio,+LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陽性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | 靈敏度/(1?特異度) |
| 陰性似然比(negative likelihood ratio,?LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陰性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | (1?靈敏度)/特異度 |
| 診斷比值比(diagnostic odds ratio,DOR) | 患者中診斷試劑判斷為陽性的比值與非患者中試劑判斷為陽性的比值之比,是融合靈敏度、特異度、陽性似然比和陰性似然比的綜合指標 | (a×d)/(b×c) |
| Kappa值 | 診斷試劑與金標準結果的一致性 | 無 |
| 綜合受試者工作特征曲線(symmetric receiver operator characteristic curve,SROC)及曲線下面積(the area under the curve,AUC) | 以靈敏度為y軸,1-特異度為x軸匯成的曲線,綜合評價診斷試劑的準確性 | 無 |
| Q指數 | SROC曲線與直線(靈敏度=特異度)相交處的靈敏度 | 無 |
| 預測性:應用診斷結果估計患者患病或不患病的可能性 | ||
| 陽性預測值(positive predictive value,PPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陽性的人數中患者的比例 | a/(a+b) |
| 陰性預測值(negative predictive value,NPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陰性的人數中非患者的比例 | d/(c+d) |
3 討論
診斷試劑是輔助臨床診療的重要手段,因為在臨床診療過程中,由于許多疾病的標準診斷方法復雜、可能給患者造成創傷、需要復雜的實驗室設備等,醫務人員在臨床診斷疾病時可能不采用金標準,而用診斷試劑替代。診斷試劑是否能準確判斷患者或非患者,將對后續的臨床診療方案產生重要影響,因此,除關注診斷試劑的技術特性、安全性和經濟性等特征外,必須將其與金標準進行比較,以評價診斷性能。
研究者可通過開展病例-對照研究、隊列研究,評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能,使所有研究對象同步、獨立、盲法進行診斷試劑和金標準的檢測[142]。然而,由于研究對象特征、樣本量等因素的影響,針對同一研究問題,不同研究者得出的結論可能存在差異,此時可利用系統評價得出綜合結論。根據證據金字塔可類推[7],診斷試劑系統評價的證據等級高于單個研究,因此,診斷試劑系統評價使用的評價指標是否全面,將直接影響對診斷試劑性能的綜合判斷。
基于本研究結果,已發表的診斷試劑系統評價使用的評價指標以靈敏度、特異度和AUC為主。靈敏度又稱真陽性率,是指實際患病且診斷試劑判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現患者的能力,該取值越大越好[6];與之對應的評價指標則是特異度,是指實際未患病且診斷試劑判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現非患者的能力,該取值越大越好[6]。診斷試劑系統評價中的SROC曲線是性能的總體表現,是對同一檢測指標的多個不同試驗進行Meta分析、根據效應量權重獲得的曲線,AUC是SROC曲線下面積,與靈敏度、特異度有關,該取值越大越好[142]。上述3個指標側重評價診斷試劑判斷結果與金標準的符合程度,但僅使用上述指標,不能全面評價診斷試劑性能。例如評價診斷試劑判斷結果與金標準的一致性,需使用Kappa值;評價診斷試劑的預測價值,需使用陽性預測值和陰性預測值。英國國家健康與臨床卓越研究所[143]、伊朗馬什哈德大學核醫學研究中心[144]分別于2011年、2016年發布指導診斷試驗系統評價的實踐指南,提及的評價指標除靈敏度、特異度和AUC外,還包括似然比、預測值和診斷比值比,上述指標均包含在表3指標體系清單中。
然而,已發表的診斷試劑系統評價使用較少的評價指標,如:Q指數、假陽性率、假陰性率、約登指數和Kappa值,在全面評價診斷試劑性能時仍具有一定作用。Q指數是SROC曲線與直線(靈敏度=特異度)相交處的靈敏度,該取值越大越好;假陽性率和假陰性率可分別用于衡量診斷試劑的誤診和漏診能力,該取值越小越好;約登指數是診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的總能力,取值范圍為0~1,常用于不同診斷試劑間的比較,該取值越大越好;Kappa值反映診斷試劑與金標準結果的一致性,取值范圍為0~1,≥0.75表示一致性較高。
本研究的局限:① 檢索字段僅限制在標題,可能遺漏部分文獻;② 限于語言限制,僅納入中、英文文獻;③ 部分文獻因無法獲得全文,暫未納入。
綜上所述,系統評價診斷試劑相較于金標準的性能時,僅使用單一指標不能全面反映診斷性能,應在數據可及的情況下,從真實性、預測性兩個維度開展評價,各維度選擇評價內容不同的指標,呈互補關系的指標選則其一即可,例如真實性維度有評價指標12個,但由于靈敏度與假陰性率互補,即靈敏度=1?假陰性率,從中選擇1個指標即可。后續仍需基于專家共識形成診斷試劑性能評價的技術指南,以規范診斷試劑性能評價指標報告模式。
![]() 表1 納入文獻的基本特征
表1 納入文獻的基本特征
| 納入研究 | 診斷藥品/試劑 | 診斷用途 | 金標準 | 應用途徑 |
| Launois 2014[8] | 結直腸癌糞便潛血試驗診斷試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 體外 | |
| Maze 2019[9] | 鉤端螺旋體病全細胞側流式檢測試劑 | 鉤端螺旋體感染 | 鉤端螺旋體培養、顯微鏡凝集試驗、聚合酶聯反應(polymerase chain reaction,PCR) | 體外 |
| Hung 2023[10] | 輪狀病毒免疫層析抗原檢測試劑 | 輪狀病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Pinson 1991[12] | Technetium-99m-RBC靜脈造影劑 | 下肢深靜脈血栓 | 其他靜脈造影劑(具體不詳) | 體內 |
| Patel 2000[13] | 陰道毛滴蟲病酶聯免疫吸附實驗(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)、直接熒光抗體 (direct fluorescent antibody,DFA)檢測試劑 | 陰道毛滴蟲病 | 滴蟲培養 | 體外 |
| Cruciani 2004[14] | Parasight?-F試紙條(Becton Dickinson) | 惡性瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2004[15] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、 血清學、PCR涂片 |
體外 |
| 郭銀燕2005[16] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、快速脲酶試驗、呼氣試驗 | 體外 |
| Blacksell 2006[17] | 登革熱免疫層析法檢測試劑(Panbio Pty Ltd.) | 登革熱 | ELISA檢測試劑(Panbio Duo,Panbio IgM,MRL IgM,AFRIMS MAC)和 | 體外 |
| Gisbert 2006[18] | 幽門螺桿菌感染糞便抗原檢測試劑 | 幽門螺桿菌感染 | 快速脲酶試驗、組織學、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學 | 體外 |
| 秦莉 2007[19] | 血清抗核小體抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 系統性紅斑狼瘡 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Steingart 2007[20] | 血清學抗體檢測試劑 | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2007[21] | 結核菌素皮膚試驗(tuberculin skin test,TST) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| 基于 ESAT-6 和 CFP-10 抗原的γ-干擾素釋放試驗 (interfering gamma release assay,IGRA) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| 王睿2008[22] | 血清神經元烯醇化酶酶免法(enzyme immunoassay,EIA)檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Pai 2008[23] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| 孟存仁2009[24] | Em18抗原ELISA檢測試劑 | 泡球蚴病 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| 楊渭臨2010[25] | 血清胃泌素釋放前體肽ELISA檢測試劑 | 小細胞肺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Branco 2010[26] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘黏性小腸梗阻 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Tucker 2010[27] | 梅毒免疫層析試紙 | 梅毒 | 血清反應素試驗、密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| 耿哲2011[28] | 血清半乳甘露聚糖ELISA檢測試劑 | 侵襲性曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Machingaidze 2011[29] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Cattamanchi 2011[30] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2011[31] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sester 2011[32] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Abba 2011[33] | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾快速檢測試劑盒 | 惡性瘧原蟲瘧疾 | 鏡檢、PCR | 體外 |
| Afonso 2012[34] | 急、慢性恰加斯病IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 急、慢性恰加斯病 | 多種確診方法(未具體描述) | 體外 |
| Shivkumar 2012[35] | 丙型肝炎快速和即時抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | PCR、免疫測定 | 體外 |
| Lamoth 2012[36] | β-葡聚糖抗原性測定試劑 | 侵入性霉菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chiappini 2012[37] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Fan 2012[38] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| TST | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體內 | |
| Santin 2012[39] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Sinclair 2013[40] | 肺炎球菌抗原檢測試劑 | 社區獲得性肺炎 | 細菌培養、臨床癥狀、X線、痰涂片鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Sollai 2014[41] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Ruizendaal 2014[42] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Boelaert 2014[43] | 內臟利什曼疾病快速診斷試劑 | 內臟利什曼疾病 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、血清學、治療反應 | 體外 |
| Khuroo 2014[44] | 乙型肝炎表面抗原(HBsAg)快速即時診斷檢測試劑 | 乙型肝炎 | 體外 | |
| Tsapas 2014[45] | 某種膏藥 | 糖尿病神經病變 | 體外 | |
| Khuroo 2015[46] | 丙型肝炎即時診斷試劑 | 丙型肝炎 | 重組免疫母細胞試驗、HCVRNA檢測 | 體外 |
| Zhou 2015[47] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 肺外結核 | 細菌培養、PCR、病理學 | 體外 |
| Aggarwal 2015[48] | IGRA(QFT-G、QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 胸膜結核 | 細菌培養、病理學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Campbell 2015[49] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-G) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Campbell 2015[50] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Chartrand 2015[51] | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染快速抗原檢測試劑 | 呼吸道合胞病毒感染 | 病毒培養、PCR、免疫熒光 | 體外 |
| Ferguson 2015[52] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷(結合病患者接觸史、X胸片、結 核病既往史) |
體外 | |
| Nicholson 2015[53] | PROGENSA前列腺癌抗原3檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學、前列腺特異性抗原水平檢測、直腸指檢、磁共振成像和臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ochodo 2015[54] | 血吸蟲病循環抗原檢測試劑和尿試紙 | 血吸蟲病 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Bechet 2016[55] | 埃文斯藍色染料 | 氣管切開術患者口咽誤吸 | 視頻透視、光纖內鏡吞咽 | 體內 |
| Leeflang 2016[56] | 萊姆病ELISA血清檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Sun 2016[57] | 血小板因子4/肝素ELISA檢測試劑 | 肝素誘導的血小板較少癥 | 臨床評估、實驗室功能測定 | 體外 |
| Waddell 2016[58] | 萊姆病ELISA檢測試劑 | 萊姆病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Cadieux 2016[59] | 丙型肝炎病毒感染抗體檢測試劑 | 丙型肝炎病毒感染 | RNA檢測、其他免疫檢測方法 | 體外 |
| Ceresoli 2016[60] | 水溶性造影劑 | 粘連性腸梗阻 | X線 | 體內 |
| Nevis 2016[61] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 過敏性鼻炎 | 鼻激發試驗 | 體內 |
| Huo 2016[62] | IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-GIT) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Kahwati 2016[63] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(T-SPOT.TB、QFT-G、QFT-GIT) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Lu 2016[64] | TST | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-IT、T-SPOT) | 結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Koski 2017[65] | 流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR、病毒培養 | 體外 |
| Cuomo 2017[66] | 皮膚點刺試驗過敏原 | 牛奶過敏 | 口服食物 | 體內 |
| Merckx 2017[67] | 甲型和乙型流感快速診斷試劑 | 甲型和乙型流感 | PCR | 體外 |
| Wijedoru 2017[68] | 傷寒和副傷寒快速診斷試劑 | 傷寒和副傷寒 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 李文 2018[69] | 葉酸受體介導的宮頸特殊染色劑 | 宮頸癌篩查 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Ning 2018[70] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染ELISA快速檢測試劑盒 | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染 | 細菌培養、鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Orme 2018[71] | 馬爾尼菲籃狀菌感染熒光酶免疫分析試 劑盒 |
結締組織病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Faust 2018[72] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-G、GFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Greenaway 2018[73] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-2G、QFT-3G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Pin Vieito 2018[74] | 結直腸癌糞便免疫化學定量檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| Wen 2018[75] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 抗酸染色、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Willemse 2018[76] | TST、抗酸染色試劑 | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| IGRA | 非結核分枝桿菌性頸面部淋巴結炎 | 病理學 | 體外 | |
| Yerlikaya 2018[77] | 瘧疾快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| Treglia 2019[78] | PET/CT示蹤劑,包括:氟-18氟脫氧葡萄糖[(18)F-FDG]、碳-11甲硫氨酸[(11)c-甲硫氨酸]、氟-18氟乙基酪氨酸[(18)F-FET]、氟-18二羥基苯丙氨酸[(18)F-FDOPA]、氟-18氟胸腺嘧啶[(18)F-FLT]和碳-11膽堿[(11)c-膽堿] | 腦腫瘤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Zanetti 2019[79] | 抗利什曼病抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 皮膚利什曼病 | Montenegro皮膚試驗、鏡檢、培養、PCR | 體外 |
| 高波 2019[80] | 示蹤劑(99mTc-亞錫植酸鈉和美蘭) | 乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢示蹤 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2019[81] | 糞便隱血檢測試劑 | 胃腸道疾病(腹痛、腹瀉、便秘和缺鐵性貧血等) | 內窺鏡、結腸鏡、糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Stonestreet 2019[82] | 糞便免疫化學血紅蛋白檢測試劑 | 結直腸癌 | 結直腸鏡 | 體外 |
| V?rhendi 2020[83] | 幽門螺桿菌診斷試劑,包括快速尿素酶試驗、尿素呼氣試驗、血清學、糞便抗原試驗 | 消化性潰瘍出血 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Jullien 2020[84] | 鼠疫快速檢測試劑 | 鼠疫 | 細菌培養、PCR、配對血清學 | 體外 |
| Volpe Chaves 2020[85] | 曲霉特異性IgG抗體ELISA檢測試劑 | 慢性肺曲霉菌病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Khandker 2021[86] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Kim 2021[87] | 甲苯胺藍 | 口腔癌及癌前病變 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Lee 2021[88] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lee 2021[89] | Quidel Sofia快速流感熒光免疫分析法診 斷試劑 |
甲型或乙型流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2021[90] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 活動性結核病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Zefenkey 2021[91] | 碳青霉烯酶快速檢測試劑 | 產碳青霉烯酶腸桿菌感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yang 2021[92] | 全氟丁烷超聲造影劑 | 肝細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Yoon 2021[93] | 諾如病毒免疫層析檢測試劑 | 諾如病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Alabousi 2021[94] | 腸內造影劑 | 成人穿透性外傷腹部骨盆CT | 手術、臨床或影像學隨訪 | 體內 |
| Albaharna 2021[95] | 局部鼻內熒光素 | 診斷和定位鼻腦脊液泄漏 | 實驗室檢查、放射學檢查 | 體內 |
| Alberts 2021[96] | 放射示蹤劑 | 復發性前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Angel-Müller 2021[97] | 梅毒即時檢測試劑 | 梅毒 | 密螺旋體和非密螺旋體試驗 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2021[98] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Okpua 2021[99] | 前列腺特異性抗原檢測試劑 | 前列腺癌 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Lima 2021[100] | 自體熒光劑 | 口腔鱗狀細胞癌 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Oh 2021[101] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2021[102] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[103] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Danwang 2021[104] | 瘧疾超靈敏快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | PCR | 體外 |
| Fairley 2021[105] | 類鼻疽病ELISA檢測試劑 | 類鼻疽病 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| 程曉2022[106] | 重組結核桿菌融合蛋白(EC) | 結核分枝桿菌感染和結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| Arshadi 2022[107] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Labiste 2022[108] | 含釓造影劑 | 闌尾骨骼骨髓炎 | 臨床特征、手術、組織學、病理學 | 體內 |
| Zhang 2022[109] | T-SPOT.TB | 結核性胸膜炎 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Brümmer 2022[110] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、細胞培養 | 體外 |
| Candia-Puma 2022[111] | 恰加斯病ELISA檢測試劑 | 恰加斯病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Chen 2022[112] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Duncan 2022[113] | SARS-CoV-2核酸擴增檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、逆轉錄酶環介導的等溫擴增、轉錄介導擴增 | 體外 |
| Falconer 2022[114] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Frempong 2022[115] | 傷寒快速診斷測試檢測試劑 | 傷寒 | 血液培養 | 體外 |
| Fujita-Rohwerder 2022[116] | SARS-CoV-2快速即時抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR、臨床癥狀、臨床隨訪 | 體外 |
| Gentilotti 2022[117] | 急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染即時檢測 試劑 |
急性社區獲得性下呼吸道感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Muzembo 2022[118] | 霍亂快速診斷檢測試劑 | 霍亂 | 糞便培養 | 體外 |
| Pandey 2022[119] | SARS-CoV-2抗原檢測快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Petnak 2022[120] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 涂片陰性肺結核 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Ren 2022[121] | IGRA | 骨關節結核 | 病理學 | 體外 |
| Romero 2022[122] | 麻風病即時診斷檢測試劑 | 麻風病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Seid 2022[123] | 脂阿拉伯甘露聚糖(LAM)抗原檢測試劑 | 結核病 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Shi 2022[124] | TBAg刺激的IFN-γ(IGRA)和未刺激的IFN-γ檢測 | 結核性腦膜炎 | 細菌培養 | 體外 |
| Shim 2022[125] | SARS-CoV-2抗原快速診斷檢測 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dinnes 2022[126] | SARS-CoV-2感染快速診斷試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Jullien 2022[127] | Luminex NxTAG RPP?(多重呼吸道病原體檢測試劑) | 呼吸道合胞病毒或甲/乙流感病毒感染 | PCR | 體外 |
| Khalid 2022[128] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Lippi 2022[129] | DiaSorin聯合SARS-CoV-2抗原免疫測定 試劑 |
SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Ma 2022[130] | 放射性示蹤劑 | 前列腺癌生化復發 | 病理學 | 體內 |
| Mahon 2022[131] | TST | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-G、T-SPOT.TB) | 潛伏性結核感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 | |
| Teeuw 2022[132] | 尿試紙 | 子癇前期蛋白尿 | PCR、24小時尿液采集中蛋白質含量≥ 300 mg |
體外 |
| Wen 2022[133] | IGRA(QFT-GIT、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核性腦膜炎 | 鏡檢、細菌培養、PCR | 體外 |
| Xie 2022[134] | SARS-CoV-2快速抗原檢測試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Yimam 2022[135] | 瘧疾新型超敏快速診斷檢測試劑、常規快速診斷檢測試劑 | 瘧疾 | 鏡檢 | 體外 |
| 鄒小青2023[136] | QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB | 活動性結核病 | 病原學、臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Ortiz-Brizuela 2023[137] | IGRA(QFT-Plus、QFT-Plus CLIA、QIAreach 、Wantai TB-IGRA、Standard E TB-Feron、T-SPOT.TB/T-Cell Select) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 臨床診斷 | 體外 |
| Karlafti 2023[138] | SARS-CoV-2鼻腔快速抗原自檢試劑 | SARS-CoV-2 | PCR | 體外 |
| Dagens 2023[139] | 埃博拉病毒快速診斷試驗檢測試劑 | 埃博拉病毒 | PCR | 體外 |
| Zhang 2023[140] | TST | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體內 |
| IGRA(QFT-GIT、QFT-Plus、T-SPOT.TB) | 結核分枝桿菌感染 | 細菌培養 | 體外 | |
| Zangiabadian 2023[141] | 艱難梭菌快速診斷檢測試劑 | 艱難梭菌感染 | 產毒培養 | 體外 |
下載CSV
![]() 表3 診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標體系
表3 診斷試劑系統評價的性能評價指標體系
| 評價維度與指標 | 指標含義 | 計算公式 |
| 真實性:診斷結果與金標準相符合的程度 | ||
| 靈敏度(真陽性率或敏感度)(sensitivity,Sen) | 診斷試劑將患者正確判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現患者的能力 | a/(a+c) |
| 假陰性率(漏診率)(false negative rate,FNR) | 診斷試劑將患者錯誤判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑漏診患者的能力 | c/(a+c) |
| 特異度(真陰性率)(specificity,Spe) | 診斷試劑將非患者正確判斷為陰性的比例,反映診斷試劑發現非患者的能力 | d/(b+d) |
| 假陽性率(誤診率)(false positive rate,FPR) | 診斷試劑將非患者錯誤判斷為陽性的比例,反映診斷試劑誤診患者的能力 | b/(b+d) |
| 符合率(一致率或準確率)(accuracy,Ac) | 診斷試劑正確判斷患者、非患者的人數占總人數的比例,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的能力 | (a+d)/(a+b+c+d) |
| 約登指數(正確指數)(Youden's index) | 靈敏度與特異度之和減1,反映診斷試劑正確判斷患者和非患者的總能力 | 靈敏度+特異度?1 |
| 陽性似然比(positive likelihood ratio,+LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陽性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | 靈敏度/(1?特異度) |
| 陰性似然比(negative likelihood ratio,?LR) | 患者中經診斷試劑判斷為陰性的概率與非患者中出現相應結果的比值,是同時反映靈敏度和特異度的復合指標 | (1?靈敏度)/特異度 |
| 診斷比值比(diagnostic odds ratio,DOR) | 患者中診斷試劑判斷為陽性的比值與非患者中試劑判斷為陽性的比值之比,是融合靈敏度、特異度、陽性似然比和陰性似然比的綜合指標 | (a×d)/(b×c) |
| Kappa值 | 診斷試劑與金標準結果的一致性 | 無 |
| 綜合受試者工作特征曲線(symmetric receiver operator characteristic curve,SROC)及曲線下面積(the area under the curve,AUC) | 以靈敏度為y軸,1-特異度為x軸匯成的曲線,綜合評價診斷試劑的準確性 | 無 |
| Q指數 | SROC曲線與直線(靈敏度=特異度)相交處的靈敏度 | 無 |
| 預測性:應用診斷結果估計患者患病或不患病的可能性 | ||
| 陽性預測值(positive predictive value,PPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陽性的人數中患者的比例 | a/(a+b) |
| 陰性預測值(negative predictive value,NPV) | 診斷試劑判斷為陰性的人數中非患者的比例 | d/(c+d) |
下載CSV
| 1. | 國家食品藥品監督管理局. 關于劃歸醫療器械管理的體外診斷試劑注冊事宜的通知(國食藥監械〔2003〕140號). 2003. |
| 2. | 國家藥品監督管理局. 醫療器械監督管理條例. 2021. |
| 3. | 國家市場監督管理總局. 體外診斷試劑注冊與備案管理辦法(國家市場監督管理總局令第48號公布). 2021. |
| 4. | 國家藥品監督管理局. 國家藥監局關于發布《體外診斷試劑分類規則》的公告(2021年第129號). 2021. |
| 5. | 《中國國家處方集》編委會. 中國國家處方集(化學藥品與生物制品卷)(第2版). 北京: 科學出版社, 2020. |
| 6. | 李立明. 流行病學(第一卷)(第3版). 北京: 人民衛生出版社, 2015. |
| 7. | 李幼平. 實用循證醫學. 北京: 人民衛生出版社, 2018. |
| 8. | Launois R, Le Moine JG, Uzzan B, et al. Systematic review and bivariate/HSROC random-effect meta-analysis of immunochemical and guaiac-based fecal occult blood tests for colorectal cancer screening. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 26(9): 978-989. |
| 9. | Maze MJ, Sharples KJ, Allan KJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of leptospirosis whole-cell lateral flow assays: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2019, 25(4): 437-444. |
| 10. | Hung PJ, Chen CC. Diagnostic accuracy of rotavirus antigen tests in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trop Med Int Health, 2023, 28(2): 72-79. |
| 11. | Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ, 2017, 358: j4008. |
| 12. | Pinson AG, Becker DM, Philbrick JT, et al. Technetium-99m-RBC venography in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremity: a systematic review of the literature. J Nucl Med. 1991, 32(12): 2324-2328. |
| 13. | Patel SR, Wiese W, Patel SC, et al. Systematic review of diagnostic tests for vaginal trichomoniasis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol, 2000, 8(5-6): 248-257. |
| 14. | Cruciani M, Nardi S, Malena M, et al. Systematic review of the accuracy of the ParaSight-F test in the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Med Sci Monit. 2004, 10(7): MT81-88. |
| 15. | Gisbert JP, Pajares JM. Stool antigen test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: a systematic review. Helicobacter, 2004, 9(4): 347-368. |
| 16. | 郭銀燕, 張澍田, 彭曉霞, 等. 幽門螺桿菌糞便抗原診斷方法的系統評價. 中華醫學雜志, 2005, 85(22): 1564-1567. |
| 17. | Blacksell SD, Doust JA, Newton PN, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunochromatographic assays for the detection of dengue virus IgM antibodies during acute infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2006, 100(8): 775-784. |
| 18. | Gisbert JP, de la Morena F, Abraira V. Accuracy of monoclonal stool antigen test for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2006, 101(8): 1921-1930. |
| 19. | 秦莉, 吳麗娟, 王蘭蘭, 等. ELISA法檢測血清抗核小體抗體診斷系統性紅斑狼瘡價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2007, 7(3): 204-210. |
| 20. | Steingart KR, Henry M, Laal S, et al. A systematic review of commercial serological antibody detection tests for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J, 2007, 83(985): 705-712. |
| 21. | Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, et al. A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection. Health Technol Assess, 2007, 11(3): 1-196. |
| 22. | 王睿, 湯建華, 李然, 等. EIA法檢測血清神經元特異性烯醇酶診斷小細胞肺癌價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2008, 8(10): 846-850. |
| 23. | Pai M, Zwerling A, Menzies D. Systematic review: T-cell-based assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: an update. Ann Intern Med, 2008, 149(3): 177-184. |
| 24. | 孟存仁, 張瓊, 張朝霞. Em18抗原ELISA法對泡球蚴病診斷價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2009, 9(7): 783-787. |
| 25. | 楊渭臨, 張薇, 章琳, 等. ELISA法檢測血清胃泌素釋放前體肽診斷小細胞肺癌的系統評價. 西安交通大學學報(醫學版), 2010, 31(6): 714-719. |
| 26. | Branco BC, Barmparas G, Schnüriger B, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic and therapeutic role of water-soluble contrast agent in adhesive small bowel obstruction. Br J Surg, 2010, 97(4): 470-478. |
| 27. | Tucker JD, Bu J, Brown LB, et al. Accelerating worldwide syphilis screening through rapid testing: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis, 2010, 10(6): 381-386. |
| 28. | 耿哲, 葉叢, 肖毅, 等. 國內ELISA血清半乳甘露聚糖檢測診斷侵襲性曲霉菌病價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2011, 11(9): 1054-1061. |
| 29. | Machingaidze S, Wiysonge CS, Gonzalez-Angulo Y, et al. The utility of an interferon gamma release assay for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection and disease in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2011, 30(8): 694-700. |
| 30. | Cattamanchi A, Smith R, Steingart KR, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr, 2011, 56(3): 230-238. |
| 31. | Chen J, Zhang R, Wang J, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2011, 6(11): e26827. |
| 32. | Sester M, Sotgiu G, Lange C, et al. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J, 2011, 37(1): 100-111. |
| 33. | Abba K, Deeks JJ, Olliaro P, et al. Rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosing uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in endemic countries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2011(7): CD008122. |
| 34. | Afonso AM, Ebell MH, Tarleton RL. A systematic review of high quality diagnostic tests for Chagas disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012, 6(11): e1881. |
| 35. | Shivkumar S, Peeling R, Jafari Y, et al. Accuracy of rapid and point-of-care screening tests for hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med, 2012, 157(8): 558-566. |
| 36. | Lamoth F, Cruciani M, Mengoli C, et al. β-Glucan antigenemia assay for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in patients with hematological malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies from the third European conference on infections in leukemia (ECIL-3). Clin Infect Dis, 2012, 54(5): 633-643. |
| 37. | Chiappini E, Accetta G, Bonsignori F, et al. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2012, 25(3): 557-564. |
| 38. | Fan L, Chen Z, Hao XH, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 2012, 65(3): 456-466. |
| 39. | Santin M, Mu?oz L, Rigau D. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e32482. |
| 40. | Sinclair A, Xie X, Teltscher M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of a urine-based pneumococcal antigen test for diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol, 2013, 51(7): 2303-2310. |
| 41. | Sollai S, Galli L, de Martino M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the utility of Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a 2013 update. BMC Infect Dis, 2014, 14(Suppl 1): S6. |
| 42. | Ruizendaal E, Dierickx S, Peeters Grietens K, et al. Success or failure of critical steps in community case management of malaria with rapid diagnostic tests: a systematic review. Malar J, 2014, 13: 229. |
| 43. | Boelaert M, Verdonck K, Menten J, et al. Rapid tests for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in patients with suspected disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2014(6): CD009135. |
| 44. | Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Khuroo MS. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care diagnostic tests for hepatitis B surface antigen-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2014, 4(3): 226-240. |
| 45. | Tsapas A, Liakos A, Paschos P, et al. A simple plaster for screening for diabetic neuropathy: a diagnostic test accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism, 2014, 63(4): 584-592. |
| 46. | Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Khuroo MS. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests for hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0121450. |
| 47. | Zhou XX, Liu YL, Zhai K, et al. Body fluid interferon-γ release assay for diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 15284. |
| 48. | Aggarwal AN, Agarwal R, Gupta D, et al. Interferon gamma release assays for diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53(8): 2451-2459. |
| 49. | Campbell JR, Krot J, Elwood K, et al. A systematic review on TST and IGRA tests used for diagnosis of LTBI in immigrants. Mol Diagn Ther, 2015, 19(1): 9-24. |
| 50. | Campbell JR, Sasitharan T, Marra F. A systematic review of studies evaluating the cost utility of screening high-risk populations for latent tuberculosis infection. Appl Health Econ Health Policy, 2015, 13(4): 325-340. |
| 51. | Chartrand C, Tremblay N, Renaud C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen detection tests for respiratory syncytial virus infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53(12): 3738-3749. |
| 52. | Ferguson TW, Tangri N, Macdonald K, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of tests for latent tuberculosis infection in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation, 2015, 99(5): 1084-1091. |
| 53. | Nicholson A, Mahon J, Boland A, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the PROGENSA? prostate cancer antigen 3 assay and the prostate health index in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess, 2015, 19(87): 1i-191i. |
| 54. | Ochodo EA, Gopalakrishna G, Spek B, et al. Circulating antigen tests and urine reagent strips for diagnosis of active schistosomiasis in endemic areas. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015(3): CD009579. |
| 55. | Béchet S, Hill F, Gilheaney ó, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the modified evan's blue dye test in detecting aspiration in patients with tracheostomy: a systematic review of the evidence. Dysphagia, 2016, 31(6): 721-729. |
| 56. | Leeflang MM, Ang CW, Berkhout J, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for Lyme borreliosis in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16: 140. |
| 57. | Sun L, Gimotty PA, Lakshmanan S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunoassays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost, 2016, 115(5): 1044-1055. |
| 58. | Waddell LA, Greig J, Mascarenhas M, et al. The accuracy of diagnostic tests for lyme disease in humans, a systematic review and meta-analysis of North American research. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0168613. |
| 59. | Cadieux G, Campbell J, Dendukuri N. Systematic review of the accuracy of antibody tests used to screen asymptomatic adults for hepatitis C infection. CMAJ Open, 2016, 4(4): E737-E745. |
| 60. | Ceresoli M, Coccolini F, Catena F, et al. Water-soluble contrast agent in adhesive small bowel obstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic value. Am J Surg, 2016, 211(6): 1114-1125. |
| 61. | Nevis IF, Binkley K, Kabali C. Diagnostic accuracy of skin-prick testing for allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol, 2016, 12: 20. |
| 62. | Huo ZY, Peng L. Accuracy of the interferon-γ release assay for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis among HIV-seropositive individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16: 350. |
| 63. | Kahwati LC, Feltner C, Halpern M, et al. Primary care screening and treatment for latent tuberculosis infection in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA, 2016, 316(9): 970-983. |
| 64. | Lu P, Chen X, Zhu LM, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung, 2016, 194(3): 447-458. |
| 65. | Koski RR, Klepser ME. A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for influenza: considerations for the community pharmacist. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003), 2017, 57(1): 13-19. |
| 66. | Cuomo B, Indirli GC, Bianchi A, et al. Specific IgE and skin prick tests to diagnose allergy to fresh and baked cow's milk according to age: a systematic review. Ital J Pediatr, 2017, 43(1): 93. |
| 67. | Merckx J, Wali R, Schiller I, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of novel and traditional rapid tests for influenza infection compared with reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med, 2017, 167(6): 394-409. |
| 68. | Wijedoru L, Mallett S, Parry CM. Rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fever. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017(5): CD008892. |
| 69. | 李文, 徐臻, 郎凱楠, 等. 宮頸特殊染色對宮頸病變篩查價值的系統評價. 現代預防醫學, 2018, 45(19): 3523-3528. |
| 70. | Ning C, Lai J, Wei W, et al. Accuracy of rapid diagnosis of Talaromyces marneffei: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0195569. |
| 71. | Orme ME, Andalucia C, Sj?lander S, et al. A comparison of a fluorescence enzyme immunoassay versus indirect immunofluorescence for initial screening of connective tissue diseases: systematic literature review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 32(4): 521-534. |
| 72. | Faust L, McCarthy A, Schreiber Y. Recommendations for the screening of paediatric latent tuberculosis infection in indigenous communities: a systematic review of screening strategies among high-risk groups in low-incidence countries. BMC Public Health, 2018, 18(1): 979. |
| 73. | Greenaway C, Pareek M, Abou Chakra CN, et al. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for latent tuberculosis among migrants in the EU/EEA: a systematic review. Euro Surveill, 2018, 23(14): 17-543. |
| 74. | Pin Vieito N, Zarraqui?os S, Cubiella J. High-risk symptoms and quantitative faecal immunochemical test accuracy: systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(19): 2383-2401. |
| 75. | Wen A, Qu XH, Zhang KN, et al. Evaluation of interferon-gamma release assays in extrasanguinous body fluids for diagnosing tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Life Sci, 2018, 197: 140-146. |
| 76. | Willemse SH, Oomens MAEM, De Lange J, et al. Diagnosing nontuberculous mycobacterial cervicofacial lymphadenitis in children: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 112: 48-54. |
| 77. | Yerlikaya S, Campillo A, Gonzalez IJ. A systematic review: performance of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of Plasmodium Knowlesi, Plasmodium Malariae, and Plasmodium Ovale monoinfections in human blood. J Infect Dis, 2018, 218(2): 265-276. |
| 78. | Treglia G, Muoio B, Trevisi G, et al. Diagnostic performance and prognostic value of PET/CT with different tracers for brain tumors: a systematic review of published meta-analyses. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(19): 4669. |
| 79. | Zanetti ADS, Sato CM, Longhi FG, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to detect anti-leishmania antibodies in patients with American tegumentary leishmaniasis: a systematic review. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo, 2019, 61: e42. |
| 80. | 高波, 魯嘉駒, 劉洋, 等. 示蹤劑注射部位對乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢診斷準確性影響的系統評價. 甘肅醫藥, 2019, 38(8): 673-682, 685. |
| 81. | Lee MW, Pourmorady JS, Laine L. Use of fecal occult blood testing as a diagnostic tool for clinical indications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(5): 662-670. |
| 82. | Stonestreet J, Chandrapalan S, Woolley D, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of faecal immunochemical testing for haemoglobin (FIT) in detecting colorectal cancer for both symptomatic and screening population. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2019, 82(2): 291-299. |
| 83. | V?rhendi N, Soós A, Anne Engh M, et al. Accuracy of the Helicobacter pylori diagnostic tests in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2020, 13: 1756284820965324. |
| 84. | Jullien S, Dissanayake HA, Chaplin M. Rapid diagnostic tests for plague. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2020, (6): CD013459. |
| 85. | Volpe Chaves CE, do Valle Leone de Oliveira SM, Venturini J, et al. Accuracy of serological tests for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2020, 15(3): e0222738. |
| 86. | Khandker SS, Nik Hashim NHH, Deris ZZ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen test kits for detecting SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 171 suspected COVID-19 patients. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(16): 3493. |
| 87. | Kim DH, Song EA, Kim SW, et al. Efficacy of toluidine blue in the diagnosis and screening of oral cancer and pre-cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol, 2021, 46(1): 23-30. |
| 88. | Lee J, Song JU, Kim YH. Diagnostic accuracy of the quidel sofia rapid influenza fluorescent immunoassay in patients with influenza-like illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul), 2021, 84(3): 226-236. |
| 89. | Lee J, Song JU, Shim SR. Comparing the diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen detection tests to real time polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Virol, 2021, 144: 104985. |
| 90. | Ma Y, Xu Y, Cao X, et al. Diagnostic value of interferon- γ release assay in HIV-infected individuals complicated with active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol Infect, 2021, 149: e204. |
| 91. | Zefenkey Z, Saleem SM, Mohammed NJ. Diagnostic accuracy of carba np test for rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae: systematic review and meta-analysis. Medico-Legal Update, 2021, 21(3): 559-569. |
| 92. | Yang Y, Liu C, Yan J, et al. Perfluorobutane contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2021, 46(10): 4619-4628. |
| 93. | Yoon SH, Kim HR, Ahn JG. Diagnostic accuracy of immunochromatographic tests for the detection of norovirus in stool specimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microbiol Spectr, 2021, 9(1): e0046721. |
| 94. | Alabousi M, Zha N, Patlas MN. Use of enteric contrast material for abdominopelvic CT in penetrating traumatic injury in adults: comparison of diagnostic accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2021, 217(3): 560-568. |
| 95. | Albaharna H, Alshareef M, Alromaih S, et al. Topical intranasal fluorescein to diagnose and localize cerebrospinal fluid leak: a systematic review. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 59(3): 223-229. |
| 96. | Alberts IL, Seide SE, Mingels C, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of radiotracers in recurrent prostate cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2021, 48(9): 2978-2989. |
| 97. | Angel-Müller E, Grillo-Ardila CF, Amaya-Guio J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for detecting active syphilis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Dis, 2021, 48(12): e202-e208. |
| 98. | Brümmer LE, Katzenschlager S, Gaeddert M, et al. Accuracy of novel antigen rapid diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med, 2021, 18(8): e1003735. |
| 99. | Okpua NC, Okekpa SI, Njaka S, et al. Clinical diagnosis of prostate cancer using digital rectal examination and prostate-specific antigen tests: a systematic review and meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity. Afr J Urol, 2021, 27(1): 32. |
| 100. | Lima IFP, Brand LM, de Figueiredo JAP, et al. Use of autofluorescence and fluorescent probes as a potential diagnostic tool for oral cancer: a systematic review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther, 2021, 33: 102073. |
| 101. | Oh CE, Ortiz-Brizuela E, Bastos ML, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of quantiFERON-TB gold plus to other tests of latent tuberculosis infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 73(5): e1116-e1125. |
| 102. | Chen CC, Lu SC, Bai CH, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests for community transmission screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(21): 11451. |
| 103. | Danwang C, Kirakoya-Samadoulougou F, Samadoulougou S. Assessing field performance of ultrasensitive rapid diagnostic tests for malaria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Malar J, 2021, 20(1): 245. |
| 104. | Danwang C, Noubiap JJ, Souopgui J, et al. Accuracy of malaria diagnostic tests performed on non-invasively collected samples: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob Health, 2021, 6(6): e005634. |
| 105. | Fairley L, Smith S, Maisrikrod S, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic tests for diagnosis of melioidosis. Acta Trop, 2021, 214: 105784. |
| 106. | 程曉, 陳哲, 焦雪峰, 等. 重組結核桿菌融合蛋白(EC)用于診斷結核分枝桿菌感染的有效性和安全性系統評價. 中國防癆雜志, 2022, 44(9): 917-926. |
| 107. | Arshadi M, Fardsanei F, Deihim B, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 detection: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 9: 870738. |
| 108. | Labiste CC, McElroy E, Subhawong TK, et al. Systematic review: investigating the added diagnostic value of gadolinium contrast agents for osteomyelitis in the appendicular skeleton. Skeletal Radiol, 2022, 51(6): 1285-1296. |
| 109. | Zhang X, Meng Q, Miao R, et al. The diagnostic value of T cell spot test and adenosine deaminase in pleural effusion for tuberculous pleurisy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2022, 135: 102223. |
| 110. | Brümmer LE, Katzenschlager S, McGrath S, et al. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care antigen-based diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression analyzing influencing factors. PLoS Med, 2022, 19(5): e1004011. |
| 111. | Candia-Puma MA, Machaca-Luque LY, Roque-Pumahuanca BM, et al. Accuracy of diagnostic tests for the detection of chagas disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(11): 2752. |
| 112. | Chen CC, Chen SY, Fang SB, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 antigen test in the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Neonatol, 2023, 64(3): 247-255. |
| 113. | Duncan DB, Mackett K, Ali MU, et al. Performance of saliva compared with nasopharyngeal swab for diagnosis of COVID-19 by NAAT in cross-sectional studies: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biochem, 2023, 117: 84-93. |
| 114. | Falconer J, Diaconu K, O'May F, et al. Cholera diagnosis in human stool and detection in water: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0270860. |
| 115. | Frempong SN, King N, Sagoo GS. The cost-effectiveness of using rapid diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of typhoid fever in patients with suspected typhoid fever: a systematic review. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res, 2022, 22(3): 391-397. |
| 116. | Fujita-Rohwerder N, Beckmann L, Zens Y, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for diagnosis of current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Evid Based Med, 2022, 27(5): 274-287. |
| 117. | Gentilotti E, De Nardo P, Cremonini E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests in acute community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2022, 28(1): 13-22. |
| 118. | Muzembo BA, Kitahara K, Debnath A, et al. Accuracy of cholera rapid diagnostic tests: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2022, 28(2): 155-162. |
| 119. | Pandey S, Poudel A, Karki D, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of antigen-detection rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of COVID-19 in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS Glob Public Health, 2022, 2(4): e0000358. |
| 120. | Petnak T, Eksombatchai D, Chesdachai S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 219. |
| 121. | Ren C, Tang J, Xia L. Interferon gamma release assays for diagnosis of osteoarticular tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(6): e0269234. |
| 122. | Romero CP, Castro R, do Brasil PEA, et al. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care serological tests for leprosy diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2022, 117: e220317. |
| 123. | Seid G, Alemu A, Tsedalu T, et al. Value of urine-based lipoarabinomannan (LAM) antigen tests for diagnosing tuberculosis in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. IJID Reg, 2022, 4: 97-104. |
| 124. | Shi F, Qiu X, Yu M, et al. Tuberculosis-specific antigen stimulated and unstimulated interferon-γ for tuberculous meningitis diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(8): e0273834. |
| 125. | Shim SR, Kim SJ, Hong M, et al. Diagnostic performance of antigen rapid diagnostic tests, chest computed tomography, and lung point-of-care-ultrasonography for SARS-CoV-2 compared with RT-PCR testing: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(6): 1302. |
| 126. | Dinnes J, Sharma P, Berhane S, et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2022(7): CD013705. |
| 127. | Jullien S, Fitzgerald F, Keddie S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multiplex respiratory pathogen panels for influenza or respiratory syncytial virus infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2022, 22(1): 785. |
| 128. | Khalid MF, Selvam K, Jeffry AJN, et al. Performance of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(1): 110. |
| 129. | Lippi G, Henry BM, Plebani M, et al. Systematic review of diagnostic accuracy of diasorin liaison SARS-CoV-2 antigen immunoassay. EJIFCC, 2022, 33(2): 94-104. |
| 130. | Ma W, Mao J, Yang J, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of radiotracers in prostate cancer biochemical recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(11): 7374-7385. |
| 131. | Mahon J, Beale S, Holmes H, et al. A systematic review of cost-utility analyses of screening methods in latent tuberculosis infection in high-risk populations. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 375. |
| 132. | Teeuw HM, Amoakoh HB, Ellis CA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of urine dipstick tests for proteinuria in pregnant women suspected of preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2022, 27: 123-130. |
| 133. | Wen A, Leng EL, Liu SM, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculous meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 788692. |
| 134. | Xie JW, He Y, Zheng YW, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 166, 943 suspected COVID-19 patients. Microbiol Res, 2022, 265: 127185. |
| 135. | Yimam Y, Mohebali M, Abbaszadeh Afshar MJ. Comparison of diagnostic performance between conventional and ultrasensitive rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of malaria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(2): e0263770. |
| 136. | 鄒小青, 楊崢蓉, 張麗帆, 等. T-SPOT. TB和QuantiFERON-TB診斷成人活動性結核病準確性的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2023, 23(4): 404-409. |
| 137. | Ortiz-Brizuela E, Apriani L, Mukherjee T, et al. Assessing the diagnostic performance of new commercial interferon-γ release assays for mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis, 2023, 76(11): 1989-1999. |
| 138. | Karlafti E, Tsavdaris D, Kotzakioulafi E, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 nasal rapid antigen self-test: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Life (Basel), 2023, 13(2): 281. |
| 139. | Dagens AB, Rojek A, Sigfrid L, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of rapid diagnostic tests for Ebola virus disease: a systematic review. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2023, 29(2): 171-181. |
| 140. | Zhang Y, Zhou G, Shi W, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of QuantiFERON-TB gold plus with QFT-GIT, T-SPOT. TB and TST: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2023, 23(1): 40. |
| 141. | Zangiabadian M, Ghorbani A, Nojookambari NY, et al. Accuracy of diagnostic assays for the detection of Clostridioides difficile: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Microbiol Methods, 2023, 204: 106657. |
| 142. | 田金徽, 陳杰峰. 診斷試驗系統評價/Meta分析指導手冊. 北京: 中國醫藥科技出版社, 2015. |
| 143. | National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Diagnostics assessment programme manual. 2011. |
| 144. | Ramin S, Giorgio T. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic studies: a practical guideline. Clin Transl Imaging, 2016, 5: 83-87. |
- 1. 國家食品藥品監督管理局. 關于劃歸醫療器械管理的體外診斷試劑注冊事宜的通知(國食藥監械〔2003〕140號). 2003.
- 2. 國家藥品監督管理局. 醫療器械監督管理條例. 2021.
- 3. 國家市場監督管理總局. 體外診斷試劑注冊與備案管理辦法(國家市場監督管理總局令第48號公布). 2021.
- 4. 國家藥品監督管理局. 國家藥監局關于發布《體外診斷試劑分類規則》的公告(2021年第129號). 2021.
- 5. 《中國國家處方集》編委會. 中國國家處方集(化學藥品與生物制品卷)(第2版). 北京: 科學出版社, 2020.
- 6. 李立明. 流行病學(第一卷)(第3版). 北京: 人民衛生出版社, 2015.
- 7. 李幼平. 實用循證醫學. 北京: 人民衛生出版社, 2018.
- 8. Launois R, Le Moine JG, Uzzan B, et al. Systematic review and bivariate/HSROC random-effect meta-analysis of immunochemical and guaiac-based fecal occult blood tests for colorectal cancer screening. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 26(9): 978-989.
- 9. Maze MJ, Sharples KJ, Allan KJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of leptospirosis whole-cell lateral flow assays: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2019, 25(4): 437-444.
- 10. Hung PJ, Chen CC. Diagnostic accuracy of rotavirus antigen tests in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trop Med Int Health, 2023, 28(2): 72-79.
- 11. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ, 2017, 358: j4008.
- 12. Pinson AG, Becker DM, Philbrick JT, et al. Technetium-99m-RBC venography in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremity: a systematic review of the literature. J Nucl Med. 1991, 32(12): 2324-2328.
- 13. Patel SR, Wiese W, Patel SC, et al. Systematic review of diagnostic tests for vaginal trichomoniasis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol, 2000, 8(5-6): 248-257.
- 14. Cruciani M, Nardi S, Malena M, et al. Systematic review of the accuracy of the ParaSight-F test in the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Med Sci Monit. 2004, 10(7): MT81-88.
- 15. Gisbert JP, Pajares JM. Stool antigen test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: a systematic review. Helicobacter, 2004, 9(4): 347-368.
- 16. 郭銀燕, 張澍田, 彭曉霞, 等. 幽門螺桿菌糞便抗原診斷方法的系統評價. 中華醫學雜志, 2005, 85(22): 1564-1567.
- 17. Blacksell SD, Doust JA, Newton PN, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunochromatographic assays for the detection of dengue virus IgM antibodies during acute infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2006, 100(8): 775-784.
- 18. Gisbert JP, de la Morena F, Abraira V. Accuracy of monoclonal stool antigen test for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2006, 101(8): 1921-1930.
- 19. 秦莉, 吳麗娟, 王蘭蘭, 等. ELISA法檢測血清抗核小體抗體診斷系統性紅斑狼瘡價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2007, 7(3): 204-210.
- 20. Steingart KR, Henry M, Laal S, et al. A systematic review of commercial serological antibody detection tests for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J, 2007, 83(985): 705-712.
- 21. Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, et al. A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection. Health Technol Assess, 2007, 11(3): 1-196.
- 22. 王睿, 湯建華, 李然, 等. EIA法檢測血清神經元特異性烯醇酶診斷小細胞肺癌價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2008, 8(10): 846-850.
- 23. Pai M, Zwerling A, Menzies D. Systematic review: T-cell-based assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: an update. Ann Intern Med, 2008, 149(3): 177-184.
- 24. 孟存仁, 張瓊, 張朝霞. Em18抗原ELISA法對泡球蚴病診斷價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2009, 9(7): 783-787.
- 25. 楊渭臨, 張薇, 章琳, 等. ELISA法檢測血清胃泌素釋放前體肽診斷小細胞肺癌的系統評價. 西安交通大學學報(醫學版), 2010, 31(6): 714-719.
- 26. Branco BC, Barmparas G, Schnüriger B, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic and therapeutic role of water-soluble contrast agent in adhesive small bowel obstruction. Br J Surg, 2010, 97(4): 470-478.
- 27. Tucker JD, Bu J, Brown LB, et al. Accelerating worldwide syphilis screening through rapid testing: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis, 2010, 10(6): 381-386.
- 28. 耿哲, 葉叢, 肖毅, 等. 國內ELISA血清半乳甘露聚糖檢測診斷侵襲性曲霉菌病價值的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2011, 11(9): 1054-1061.
- 29. Machingaidze S, Wiysonge CS, Gonzalez-Angulo Y, et al. The utility of an interferon gamma release assay for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection and disease in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2011, 30(8): 694-700.
- 30. Cattamanchi A, Smith R, Steingart KR, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr, 2011, 56(3): 230-238.
- 31. Chen J, Zhang R, Wang J, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2011, 6(11): e26827.
- 32. Sester M, Sotgiu G, Lange C, et al. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J, 2011, 37(1): 100-111.
- 33. Abba K, Deeks JJ, Olliaro P, et al. Rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosing uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in endemic countries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2011(7): CD008122.
- 34. Afonso AM, Ebell MH, Tarleton RL. A systematic review of high quality diagnostic tests for Chagas disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012, 6(11): e1881.
- 35. Shivkumar S, Peeling R, Jafari Y, et al. Accuracy of rapid and point-of-care screening tests for hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med, 2012, 157(8): 558-566.
- 36. Lamoth F, Cruciani M, Mengoli C, et al. β-Glucan antigenemia assay for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in patients with hematological malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies from the third European conference on infections in leukemia (ECIL-3). Clin Infect Dis, 2012, 54(5): 633-643.
- 37. Chiappini E, Accetta G, Bonsignori F, et al. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2012, 25(3): 557-564.
- 38. Fan L, Chen Z, Hao XH, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 2012, 65(3): 456-466.
- 39. Santin M, Mu?oz L, Rigau D. Interferon-γ release assays for the diagnosis of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e32482.
- 40. Sinclair A, Xie X, Teltscher M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of a urine-based pneumococcal antigen test for diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol, 2013, 51(7): 2303-2310.
- 41. Sollai S, Galli L, de Martino M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the utility of Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a 2013 update. BMC Infect Dis, 2014, 14(Suppl 1): S6.
- 42. Ruizendaal E, Dierickx S, Peeters Grietens K, et al. Success or failure of critical steps in community case management of malaria with rapid diagnostic tests: a systematic review. Malar J, 2014, 13: 229.
- 43. Boelaert M, Verdonck K, Menten J, et al. Rapid tests for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in patients with suspected disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2014(6): CD009135.
- 44. Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Khuroo MS. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care diagnostic tests for hepatitis B surface antigen-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2014, 4(3): 226-240.
- 45. Tsapas A, Liakos A, Paschos P, et al. A simple plaster for screening for diabetic neuropathy: a diagnostic test accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism, 2014, 63(4): 584-592.
- 46. Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Khuroo MS. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests for hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0121450.
- 47. Zhou XX, Liu YL, Zhai K, et al. Body fluid interferon-γ release assay for diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 15284.
- 48. Aggarwal AN, Agarwal R, Gupta D, et al. Interferon gamma release assays for diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53(8): 2451-2459.
- 49. Campbell JR, Krot J, Elwood K, et al. A systematic review on TST and IGRA tests used for diagnosis of LTBI in immigrants. Mol Diagn Ther, 2015, 19(1): 9-24.
- 50. Campbell JR, Sasitharan T, Marra F. A systematic review of studies evaluating the cost utility of screening high-risk populations for latent tuberculosis infection. Appl Health Econ Health Policy, 2015, 13(4): 325-340.
- 51. Chartrand C, Tremblay N, Renaud C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen detection tests for respiratory syncytial virus infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53(12): 3738-3749.
- 52. Ferguson TW, Tangri N, Macdonald K, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of tests for latent tuberculosis infection in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation, 2015, 99(5): 1084-1091.
- 53. Nicholson A, Mahon J, Boland A, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the PROGENSA? prostate cancer antigen 3 assay and the prostate health index in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess, 2015, 19(87): 1i-191i.
- 54. Ochodo EA, Gopalakrishna G, Spek B, et al. Circulating antigen tests and urine reagent strips for diagnosis of active schistosomiasis in endemic areas. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015(3): CD009579.
- 55. Béchet S, Hill F, Gilheaney ó, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the modified evan's blue dye test in detecting aspiration in patients with tracheostomy: a systematic review of the evidence. Dysphagia, 2016, 31(6): 721-729.
- 56. Leeflang MM, Ang CW, Berkhout J, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for Lyme borreliosis in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16: 140.
- 57. Sun L, Gimotty PA, Lakshmanan S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunoassays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost, 2016, 115(5): 1044-1055.
- 58. Waddell LA, Greig J, Mascarenhas M, et al. The accuracy of diagnostic tests for lyme disease in humans, a systematic review and meta-analysis of North American research. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0168613.
- 59. Cadieux G, Campbell J, Dendukuri N. Systematic review of the accuracy of antibody tests used to screen asymptomatic adults for hepatitis C infection. CMAJ Open, 2016, 4(4): E737-E745.
- 60. Ceresoli M, Coccolini F, Catena F, et al. Water-soluble contrast agent in adhesive small bowel obstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic value. Am J Surg, 2016, 211(6): 1114-1125.
- 61. Nevis IF, Binkley K, Kabali C. Diagnostic accuracy of skin-prick testing for allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol, 2016, 12: 20.
- 62. Huo ZY, Peng L. Accuracy of the interferon-γ release assay for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis among HIV-seropositive individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16: 350.
- 63. Kahwati LC, Feltner C, Halpern M, et al. Primary care screening and treatment for latent tuberculosis infection in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA, 2016, 316(9): 970-983.
- 64. Lu P, Chen X, Zhu LM, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung, 2016, 194(3): 447-458.
- 65. Koski RR, Klepser ME. A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for influenza: considerations for the community pharmacist. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003), 2017, 57(1): 13-19.
- 66. Cuomo B, Indirli GC, Bianchi A, et al. Specific IgE and skin prick tests to diagnose allergy to fresh and baked cow's milk according to age: a systematic review. Ital J Pediatr, 2017, 43(1): 93.
- 67. Merckx J, Wali R, Schiller I, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of novel and traditional rapid tests for influenza infection compared with reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med, 2017, 167(6): 394-409.
- 68. Wijedoru L, Mallett S, Parry CM. Rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fever. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017(5): CD008892.
- 69. 李文, 徐臻, 郎凱楠, 等. 宮頸特殊染色對宮頸病變篩查價值的系統評價. 現代預防醫學, 2018, 45(19): 3523-3528.
- 70. Ning C, Lai J, Wei W, et al. Accuracy of rapid diagnosis of Talaromyces marneffei: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0195569.
- 71. Orme ME, Andalucia C, Sj?lander S, et al. A comparison of a fluorescence enzyme immunoassay versus indirect immunofluorescence for initial screening of connective tissue diseases: systematic literature review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 32(4): 521-534.
- 72. Faust L, McCarthy A, Schreiber Y. Recommendations for the screening of paediatric latent tuberculosis infection in indigenous communities: a systematic review of screening strategies among high-risk groups in low-incidence countries. BMC Public Health, 2018, 18(1): 979.
- 73. Greenaway C, Pareek M, Abou Chakra CN, et al. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for latent tuberculosis among migrants in the EU/EEA: a systematic review. Euro Surveill, 2018, 23(14): 17-543.
- 74. Pin Vieito N, Zarraqui?os S, Cubiella J. High-risk symptoms and quantitative faecal immunochemical test accuracy: systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(19): 2383-2401.
- 75. Wen A, Qu XH, Zhang KN, et al. Evaluation of interferon-gamma release assays in extrasanguinous body fluids for diagnosing tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Life Sci, 2018, 197: 140-146.
- 76. Willemse SH, Oomens MAEM, De Lange J, et al. Diagnosing nontuberculous mycobacterial cervicofacial lymphadenitis in children: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 112: 48-54.
- 77. Yerlikaya S, Campillo A, Gonzalez IJ. A systematic review: performance of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of Plasmodium Knowlesi, Plasmodium Malariae, and Plasmodium Ovale monoinfections in human blood. J Infect Dis, 2018, 218(2): 265-276.
- 78. Treglia G, Muoio B, Trevisi G, et al. Diagnostic performance and prognostic value of PET/CT with different tracers for brain tumors: a systematic review of published meta-analyses. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(19): 4669.
- 79. Zanetti ADS, Sato CM, Longhi FG, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to detect anti-leishmania antibodies in patients with American tegumentary leishmaniasis: a systematic review. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo, 2019, 61: e42.
- 80. 高波, 魯嘉駒, 劉洋, 等. 示蹤劑注射部位對乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢診斷準確性影響的系統評價. 甘肅醫藥, 2019, 38(8): 673-682, 685.
- 81. Lee MW, Pourmorady JS, Laine L. Use of fecal occult blood testing as a diagnostic tool for clinical indications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(5): 662-670.
- 82. Stonestreet J, Chandrapalan S, Woolley D, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of faecal immunochemical testing for haemoglobin (FIT) in detecting colorectal cancer for both symptomatic and screening population. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2019, 82(2): 291-299.
- 83. V?rhendi N, Soós A, Anne Engh M, et al. Accuracy of the Helicobacter pylori diagnostic tests in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2020, 13: 1756284820965324.
- 84. Jullien S, Dissanayake HA, Chaplin M. Rapid diagnostic tests for plague. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2020, (6): CD013459.
- 85. Volpe Chaves CE, do Valle Leone de Oliveira SM, Venturini J, et al. Accuracy of serological tests for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2020, 15(3): e0222738.
- 86. Khandker SS, Nik Hashim NHH, Deris ZZ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen test kits for detecting SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 171 suspected COVID-19 patients. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(16): 3493.
- 87. Kim DH, Song EA, Kim SW, et al. Efficacy of toluidine blue in the diagnosis and screening of oral cancer and pre-cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol, 2021, 46(1): 23-30.
- 88. Lee J, Song JU, Kim YH. Diagnostic accuracy of the quidel sofia rapid influenza fluorescent immunoassay in patients with influenza-like illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul), 2021, 84(3): 226-236.
- 89. Lee J, Song JU, Shim SR. Comparing the diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen detection tests to real time polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Virol, 2021, 144: 104985.
- 90. Ma Y, Xu Y, Cao X, et al. Diagnostic value of interferon- γ release assay in HIV-infected individuals complicated with active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol Infect, 2021, 149: e204.
- 91. Zefenkey Z, Saleem SM, Mohammed NJ. Diagnostic accuracy of carba np test for rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae: systematic review and meta-analysis. Medico-Legal Update, 2021, 21(3): 559-569.
- 92. Yang Y, Liu C, Yan J, et al. Perfluorobutane contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2021, 46(10): 4619-4628.
- 93. Yoon SH, Kim HR, Ahn JG. Diagnostic accuracy of immunochromatographic tests for the detection of norovirus in stool specimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microbiol Spectr, 2021, 9(1): e0046721.
- 94. Alabousi M, Zha N, Patlas MN. Use of enteric contrast material for abdominopelvic CT in penetrating traumatic injury in adults: comparison of diagnostic accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2021, 217(3): 560-568.
- 95. Albaharna H, Alshareef M, Alromaih S, et al. Topical intranasal fluorescein to diagnose and localize cerebrospinal fluid leak: a systematic review. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 59(3): 223-229.
- 96. Alberts IL, Seide SE, Mingels C, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of radiotracers in recurrent prostate cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2021, 48(9): 2978-2989.
- 97. Angel-Müller E, Grillo-Ardila CF, Amaya-Guio J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for detecting active syphilis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Dis, 2021, 48(12): e202-e208.
- 98. Brümmer LE, Katzenschlager S, Gaeddert M, et al. Accuracy of novel antigen rapid diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med, 2021, 18(8): e1003735.
- 99. Okpua NC, Okekpa SI, Njaka S, et al. Clinical diagnosis of prostate cancer using digital rectal examination and prostate-specific antigen tests: a systematic review and meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity. Afr J Urol, 2021, 27(1): 32.
- 100. Lima IFP, Brand LM, de Figueiredo JAP, et al. Use of autofluorescence and fluorescent probes as a potential diagnostic tool for oral cancer: a systematic review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther, 2021, 33: 102073.
- 101. Oh CE, Ortiz-Brizuela E, Bastos ML, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of quantiFERON-TB gold plus to other tests of latent tuberculosis infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 73(5): e1116-e1125.
- 102. Chen CC, Lu SC, Bai CH, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests for community transmission screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(21): 11451.
- 103. Danwang C, Kirakoya-Samadoulougou F, Samadoulougou S. Assessing field performance of ultrasensitive rapid diagnostic tests for malaria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Malar J, 2021, 20(1): 245.
- 104. Danwang C, Noubiap JJ, Souopgui J, et al. Accuracy of malaria diagnostic tests performed on non-invasively collected samples: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob Health, 2021, 6(6): e005634.
- 105. Fairley L, Smith S, Maisrikrod S, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic tests for diagnosis of melioidosis. Acta Trop, 2021, 214: 105784.
- 106. 程曉, 陳哲, 焦雪峰, 等. 重組結核桿菌融合蛋白(EC)用于診斷結核分枝桿菌感染的有效性和安全性系統評價. 中國防癆雜志, 2022, 44(9): 917-926.
- 107. Arshadi M, Fardsanei F, Deihim B, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 detection: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 9: 870738.
- 108. Labiste CC, McElroy E, Subhawong TK, et al. Systematic review: investigating the added diagnostic value of gadolinium contrast agents for osteomyelitis in the appendicular skeleton. Skeletal Radiol, 2022, 51(6): 1285-1296.
- 109. Zhang X, Meng Q, Miao R, et al. The diagnostic value of T cell spot test and adenosine deaminase in pleural effusion for tuberculous pleurisy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2022, 135: 102223.
- 110. Brümmer LE, Katzenschlager S, McGrath S, et al. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care antigen-based diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression analyzing influencing factors. PLoS Med, 2022, 19(5): e1004011.
- 111. Candia-Puma MA, Machaca-Luque LY, Roque-Pumahuanca BM, et al. Accuracy of diagnostic tests for the detection of chagas disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(11): 2752.
- 112. Chen CC, Chen SY, Fang SB, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 antigen test in the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Neonatol, 2023, 64(3): 247-255.
- 113. Duncan DB, Mackett K, Ali MU, et al. Performance of saliva compared with nasopharyngeal swab for diagnosis of COVID-19 by NAAT in cross-sectional studies: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biochem, 2023, 117: 84-93.
- 114. Falconer J, Diaconu K, O'May F, et al. Cholera diagnosis in human stool and detection in water: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0270860.
- 115. Frempong SN, King N, Sagoo GS. The cost-effectiveness of using rapid diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of typhoid fever in patients with suspected typhoid fever: a systematic review. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res, 2022, 22(3): 391-397.
- 116. Fujita-Rohwerder N, Beckmann L, Zens Y, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for diagnosis of current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Evid Based Med, 2022, 27(5): 274-287.
- 117. Gentilotti E, De Nardo P, Cremonini E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests in acute community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2022, 28(1): 13-22.
- 118. Muzembo BA, Kitahara K, Debnath A, et al. Accuracy of cholera rapid diagnostic tests: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2022, 28(2): 155-162.
- 119. Pandey S, Poudel A, Karki D, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of antigen-detection rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of COVID-19 in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS Glob Public Health, 2022, 2(4): e0000358.
- 120. Petnak T, Eksombatchai D, Chesdachai S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 219.
- 121. Ren C, Tang J, Xia L. Interferon gamma release assays for diagnosis of osteoarticular tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(6): e0269234.
- 122. Romero CP, Castro R, do Brasil PEA, et al. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care serological tests for leprosy diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2022, 117: e220317.
- 123. Seid G, Alemu A, Tsedalu T, et al. Value of urine-based lipoarabinomannan (LAM) antigen tests for diagnosing tuberculosis in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. IJID Reg, 2022, 4: 97-104.
- 124. Shi F, Qiu X, Yu M, et al. Tuberculosis-specific antigen stimulated and unstimulated interferon-γ for tuberculous meningitis diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(8): e0273834.
- 125. Shim SR, Kim SJ, Hong M, et al. Diagnostic performance of antigen rapid diagnostic tests, chest computed tomography, and lung point-of-care-ultrasonography for SARS-CoV-2 compared with RT-PCR testing: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(6): 1302.
- 126. Dinnes J, Sharma P, Berhane S, et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2022(7): CD013705.
- 127. Jullien S, Fitzgerald F, Keddie S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multiplex respiratory pathogen panels for influenza or respiratory syncytial virus infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2022, 22(1): 785.
- 128. Khalid MF, Selvam K, Jeffry AJN, et al. Performance of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(1): 110.
- 129. Lippi G, Henry BM, Plebani M, et al. Systematic review of diagnostic accuracy of diasorin liaison SARS-CoV-2 antigen immunoassay. EJIFCC, 2022, 33(2): 94-104.
- 130. Ma W, Mao J, Yang J, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of radiotracers in prostate cancer biochemical recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(11): 7374-7385.
- 131. Mahon J, Beale S, Holmes H, et al. A systematic review of cost-utility analyses of screening methods in latent tuberculosis infection in high-risk populations. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 375.
- 132. Teeuw HM, Amoakoh HB, Ellis CA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of urine dipstick tests for proteinuria in pregnant women suspected of preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2022, 27: 123-130.
- 133. Wen A, Leng EL, Liu SM, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculous meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 788692.
- 134. Xie JW, He Y, Zheng YW, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 166, 943 suspected COVID-19 patients. Microbiol Res, 2022, 265: 127185.
- 135. Yimam Y, Mohebali M, Abbaszadeh Afshar MJ. Comparison of diagnostic performance between conventional and ultrasensitive rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of malaria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2022, 17(2): e0263770.
- 136. 鄒小青, 楊崢蓉, 張麗帆, 等. T-SPOT. TB和QuantiFERON-TB診斷成人活動性結核病準確性的系統評價. 中國循證醫學雜志, 2023, 23(4): 404-409.
- 137. Ortiz-Brizuela E, Apriani L, Mukherjee T, et al. Assessing the diagnostic performance of new commercial interferon-γ release assays for mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis, 2023, 76(11): 1989-1999.
- 138. Karlafti E, Tsavdaris D, Kotzakioulafi E, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 nasal rapid antigen self-test: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Life (Basel), 2023, 13(2): 281.
- 139. Dagens AB, Rojek A, Sigfrid L, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of rapid diagnostic tests for Ebola virus disease: a systematic review. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2023, 29(2): 171-181.
- 140. Zhang Y, Zhou G, Shi W, et al. Comparing the diagnostic performance of QuantiFERON-TB gold plus with QFT-GIT, T-SPOT. TB and TST: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 2023, 23(1): 40.
- 141. Zangiabadian M, Ghorbani A, Nojookambari NY, et al. Accuracy of diagnostic assays for the detection of Clostridioides difficile: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Microbiol Methods, 2023, 204: 106657.
- 142. 田金徽, 陳杰峰. 診斷試驗系統評價/Meta分析指導手冊. 北京: 中國醫藥科技出版社, 2015.
- 143. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Diagnostics assessment programme manual. 2011.
- 144. Ramin S, Giorgio T. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic studies: a practical guideline. Clin Transl Imaging, 2016, 5: 83-87.